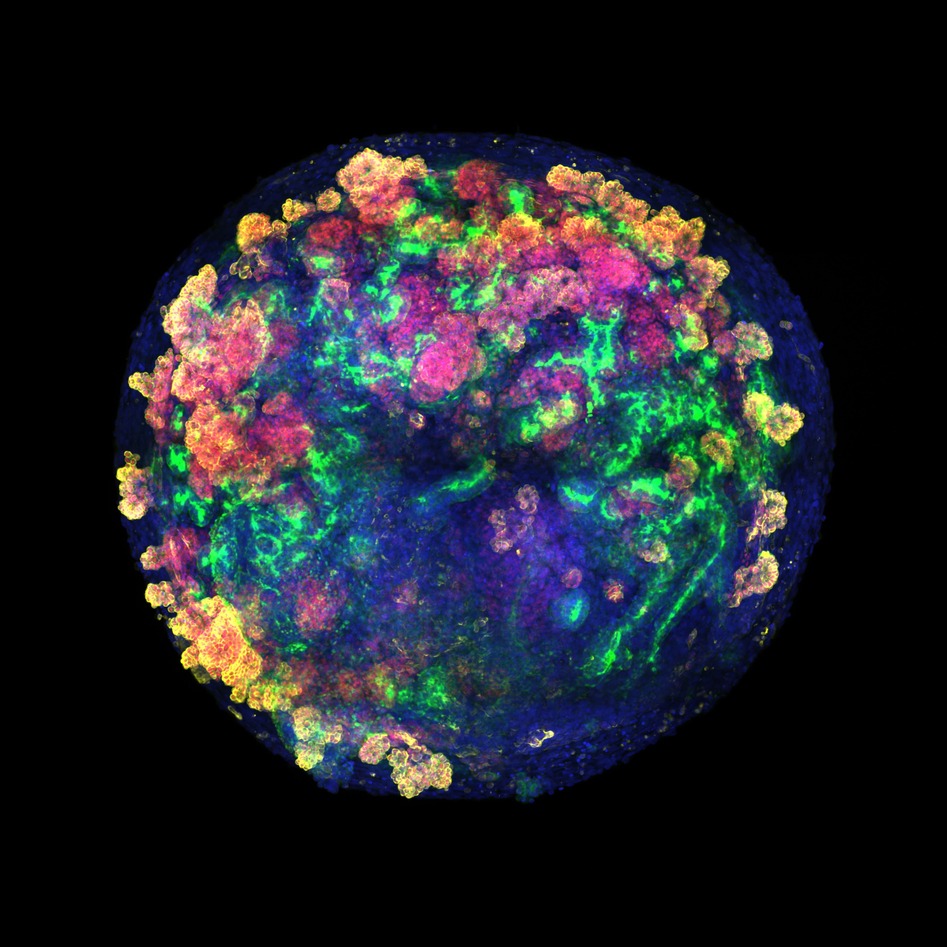
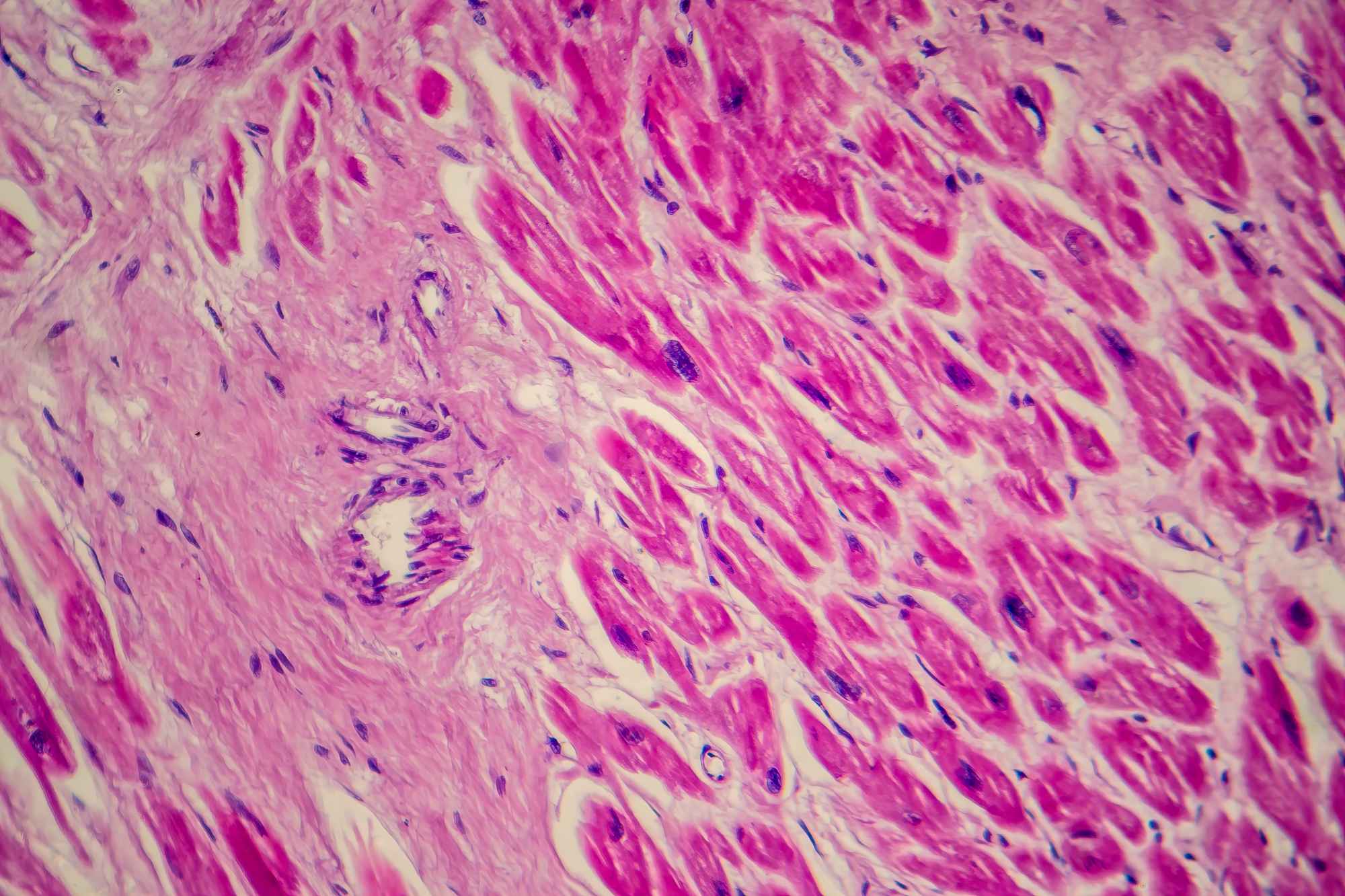
For the first time, pig kidneys modified with human renal organoids are transplanted into pigs
An international team, including several Spanish groups and coordinated by the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC), has developed a pioneering technology that allows for the creation of multiple human kidney organoids, their combination with pig kidneys outside the body, and their successful transplantation back into the same animal. The method could contribute to improving future research and, according to the authors, allows us to envision a future clinical scenario in which organs destined for transplantation can be treated and conditioned before implantation. The work is published in Nature Biomedical Engineering.