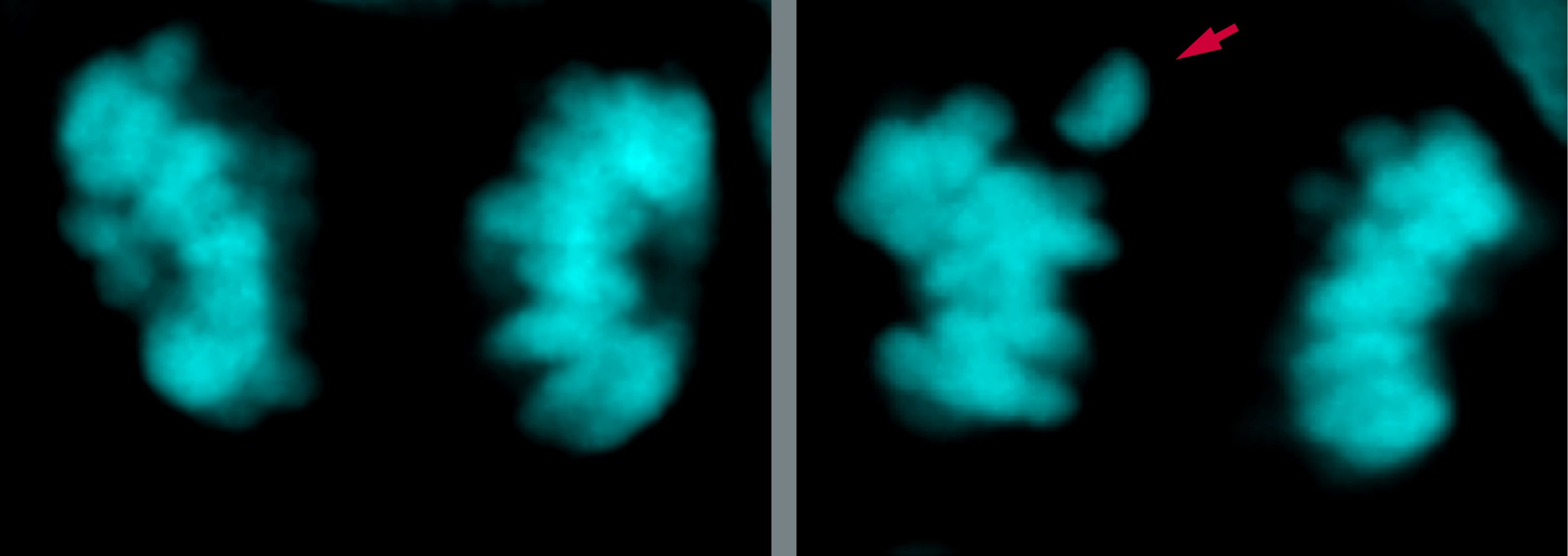
Reactions: modern humans record fewer chromosomal errors during brain development than Neanderthals and apes
Compared to Neanderthals and apes, modern humans experience fewer chromosomal inheritance errors when their brains develop, according to a new study published in Science Advances.