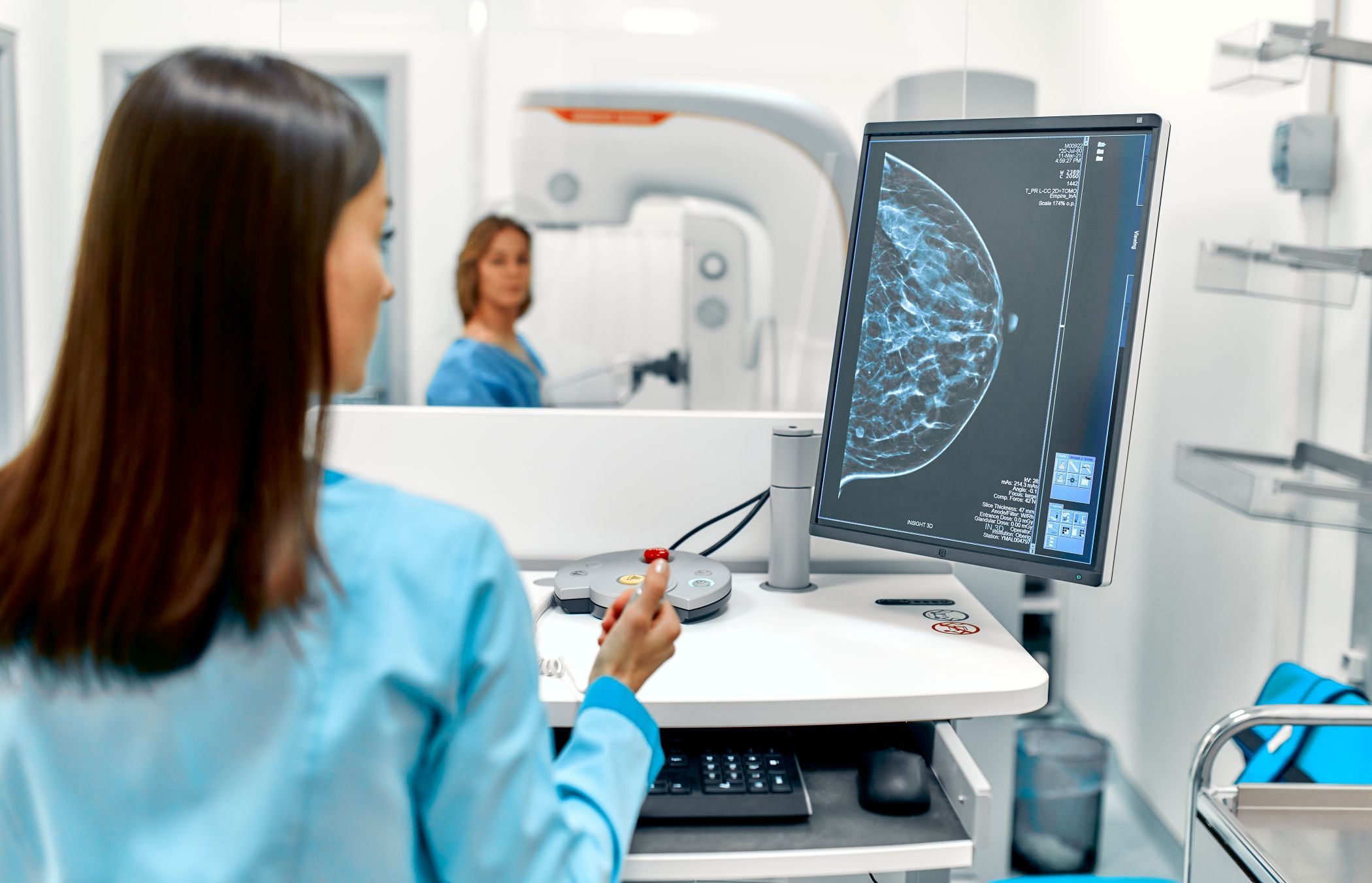
Breast cancer mortality in Spain has fallen by more than 40% over the last three decades
A study published in The Lancet Oncology shows that age-adjusted breast cancer mortality has declined from 1990 to 2023, even though the number of cases has increased. In Spain, the mortality rate for this disease fell by almost 42% during this period, reflecting the success of screening, diagnosis and treatment in high-income countries, according to the article's data. Although incidence and mortality rates will remain stable, the authors predict that population growth and ageing will increase the number of breast cancer cases and deaths between now and 2050.