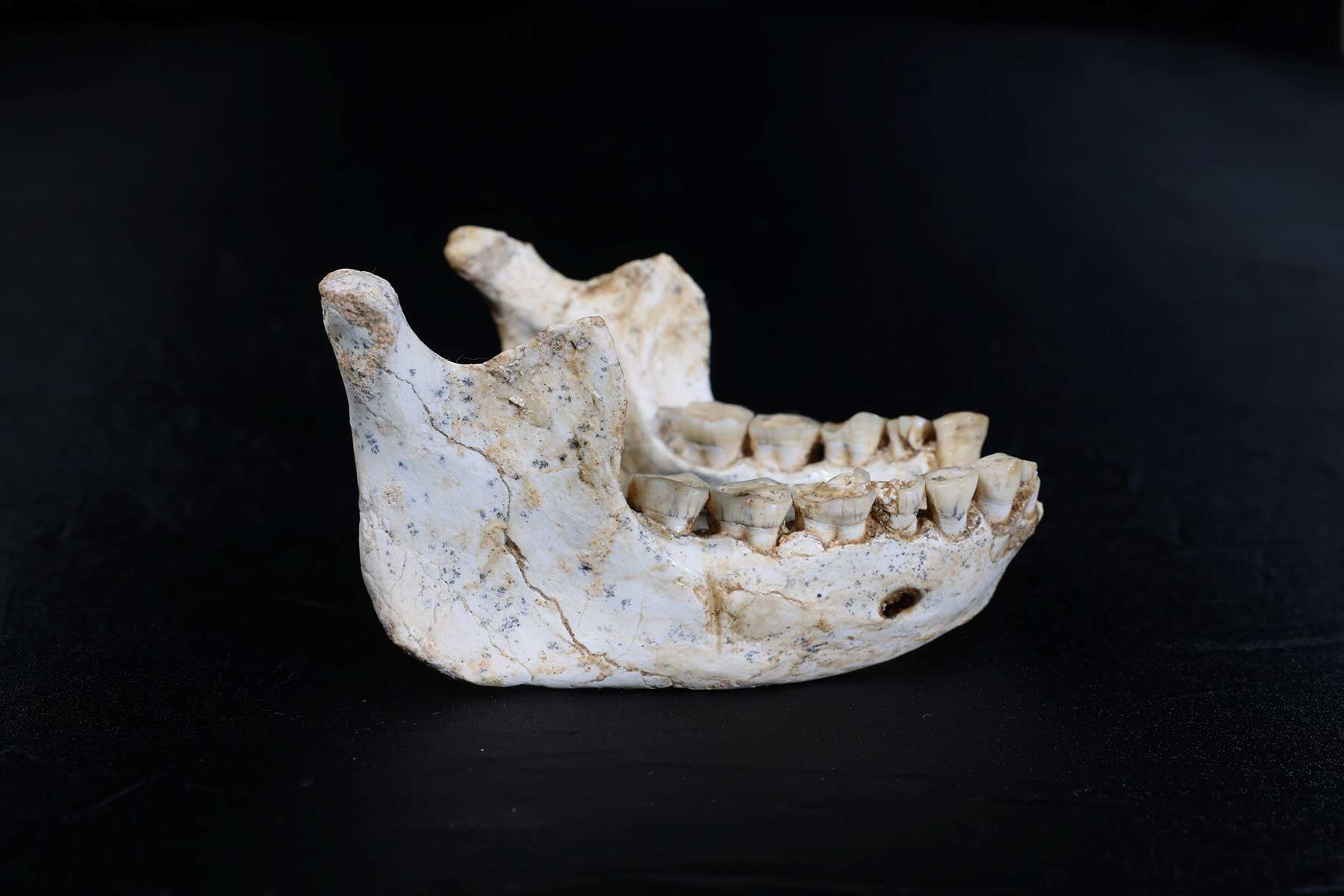
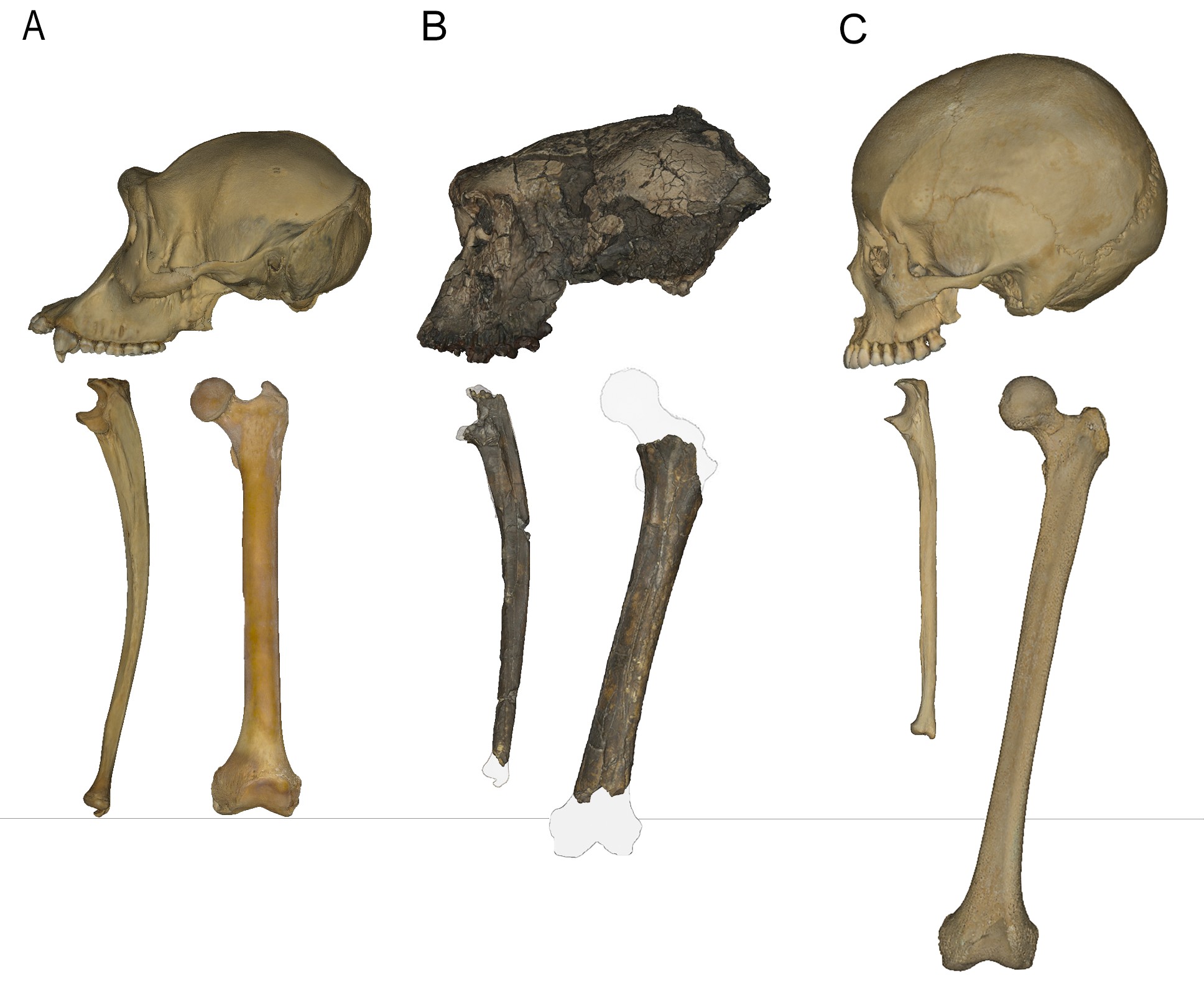
Hominid fossils discovered in Morocco could be from ancestors very close to modern humans
An international team with Spanish participation has analysed hominid remains discovered in Casablanca (Morocco) and concluded that they could be very close ancestors of early modern humans. The fossils date from around the same period as the Homo antecessor found in Atapuerca—some 773,000 years ago—but are morphologically different. According to the authors, who published their findings in Nature, the fossils offer clues about the last common ancestor shared with Neanderthals and Denisovans, and support an African, rather than Eurasian, origin for H. sapiens.