
Science journal has published a global map showing exposure to perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) through the consumption of fish products. PFAS are substances that are difficult to break down, meaning they can accumulate in the body, and some are linked to health problems. The authors collected data over 20 years from PFAS measurements in the marine environment and fisheries, and mapped the concentrations of these compounds in more than 200 species of marine fish. The study shows that international fish trade redistributes the risk of PFAS exposure from highly polluted regions to less exposed areas, with European trade playing a key role in increasing the risk of exposure to these substances.

Science magazine has chosen “the seemingly unstoppable growth of renewable energy” as the most notable scientific advance of 2025. The journal highlights that this year was the first in which solar and wind energy surpassed fossil fuel-based energy in certain areas. In this transition, Science highlights the role of China, which now dominates global production of solar panels, wind turbines, and lithium batteries, and has managed to make renewable energy technology cheaper. Among the obstacles, the magazine cites the continued widespread use of coal and political resistance in countries such as the United States.

People who ate more than 50 grams of high-fat cheese—such as cheddar, brie, or gouda—per day in the 1990s had a lower risk of dementia 25 years later than those who consumed less cheese, according to a study published in Neurology. The study is based on data from more than 27,000 people in Sweden with an average age of 58. The research also shows that those who consumed high-fat cream daily had a lower risk of dementia compared to those who did not consume it.

A team from the United States has used data from health studies to analyze the extent to which prestigious journals capture or ignore science considered influential. Their findings indicate that most of the most cited articles—thus considered most influential—are published in journals not ranked among the most prestigious. According to the study, approximately half of all researchers never publish in a journal with an impact factor above 15, which, according to certain evaluation systems, could exclude them from opportunities. However, overall, traditional journal-based measures may only recognize between 10% and 20% of influential work. The results are published in Plos Biology.

Restrictions on mobility and activity imposed during the covid-19 pandemic had an impact on the beaks of a species of bird, specifically the dark-eyed junco, which lived in urban areas of Los Angeles (USA). This is shown in a study published in the journal PNAS, which reveals how birds born during these lockdowns had beaks similar to their counterparts in the wild. With the return of human activity, the beak returned to its pre-pandemic shape. The authors argue that this change was mainly due to an adaptation to the food available, as the birds no longer had access to human food waste.

An international team has analyzed data from nearly 60 studies involving more than 48,000 children with different types of diets and compared the nutritional profile and various health parameters between those following vegan, lacto-ovo-vegetarian, and omnivorous diets. The results indicate that plant-based diets, if well-planned, can promote healthy growth with benefits such as a better cardiovascular profile and lower cholesterol levels. However, they may have difficulty achieving adequate levels of vitamins D and B12, calcium, iron, and zinc. According to the authors, the findings underscore the need for careful planning and supplementation in children following these types of diets. The study is published in Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition.
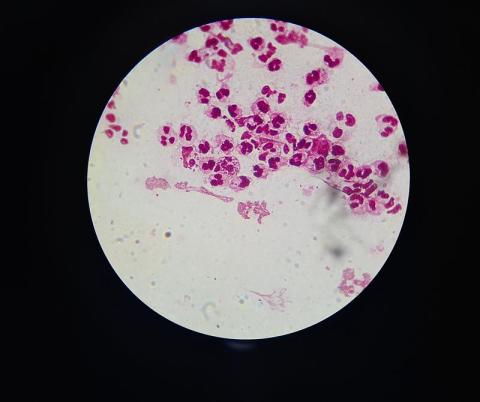
One oral dose of zoliflodacin—a new antibiotic—is as effective as the current treatment for uncomplicated urogenital gonorrhoea, according to the results of a phase 3 clinical trial published in The Lancet. In some parts of the world, the bacteria that cause gonorrhoea have developed resistance to the current treatment, which combines an injection of ceftriaxone and an oral dose of azithromycin. Zoliflodacin could be an alternative to this treatment, concludes the study, which included 900 people from five countries.

The GHGSat satellite constellation has identified 3,114 oil, gas and coal facilities worldwide that emitted 8.3 million tonnes of methane in 2023, according to data published in the journal Science. These estimates are more accurate than inventories taken on the ground or in the atmosphere.

A study published in the journal Scientific Reports reveals an increase in simplicity, negativity, and stress-related words in pop song lyrics in the United States over the last few decades. The authors also conclude that this phenomenon was attenuated in times of social crisis, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, which ‘highlights the role of music in both shaping and reflecting moods.’ The data included more than 20,000 songs from the US charts between 1973 and 2023.

A meta-analysis published in The Lancet Psychiatry journal concludes that the most effective way to discontinue antidepressant treatment in people with remitting depression is to gradually reduce the dose in combination with psychological therapy. Furthermore, this strategy proved to be just as effective in preventing relapses into depression as continuing medication. The study was based on data from more than 17,000 adults with depression and anxiety in remission, although the evidence for the latter disorder was not as robust.