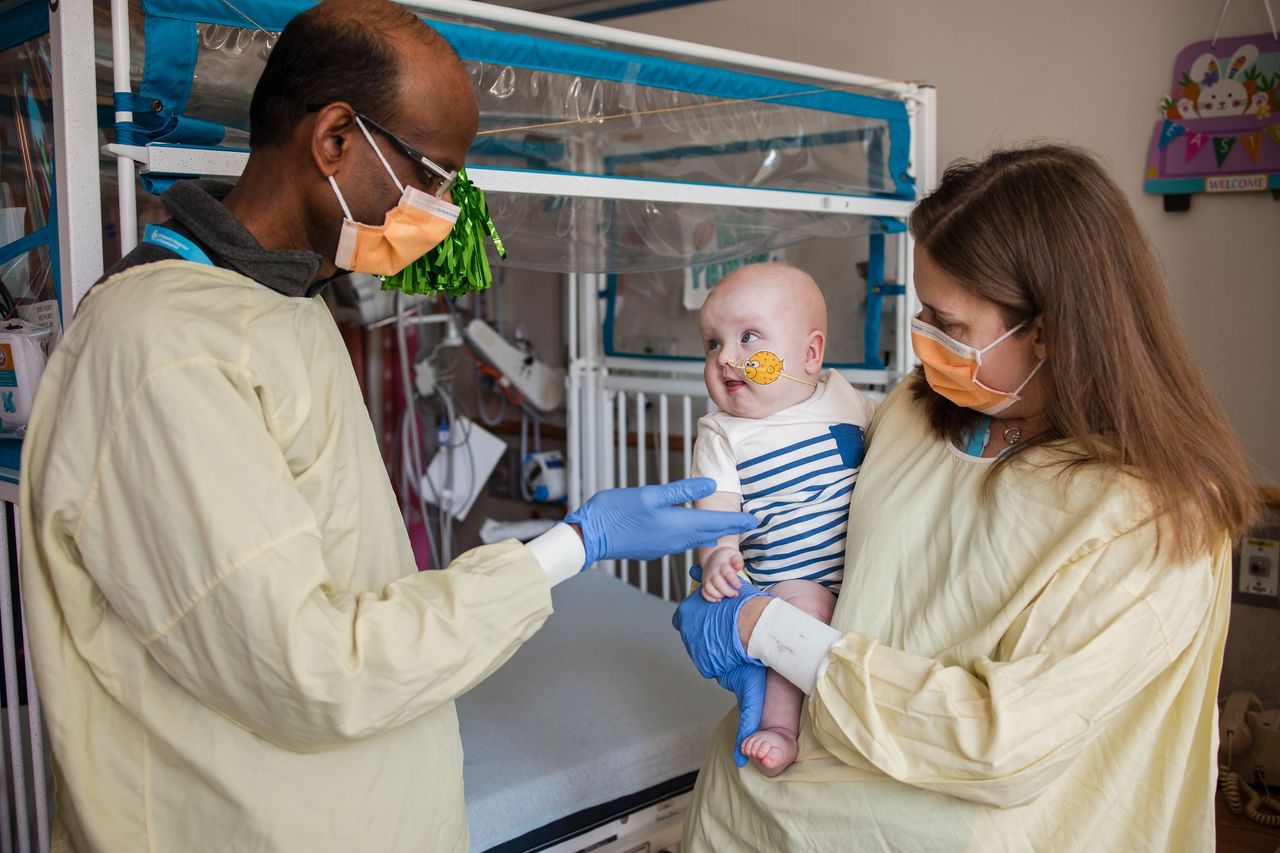
A team from the Children's Hospital of Philadelphia and Penn Medicine (United States) has successfully treated a baby diagnosed with a rare genetic disorder using personalised CRISPR gene editing therapy. The baby, known only by the initials KJ, was born with a rare metabolic disease known as severe carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1 (CPS1) deficiency. After spending the first months of his life in hospital on a very restrictive diet, KJ received the first dose of his tailored therapy in February 2025, between six and seven months of age. The treatment, which is being used for the first time for this type of disorder, was administered safely, and the baby is now growing well and improving. The case is detailed in a study published by The New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM).