Preliminary data show that measles cases in Europe declined in 2025, although they increased in countries such as Spain
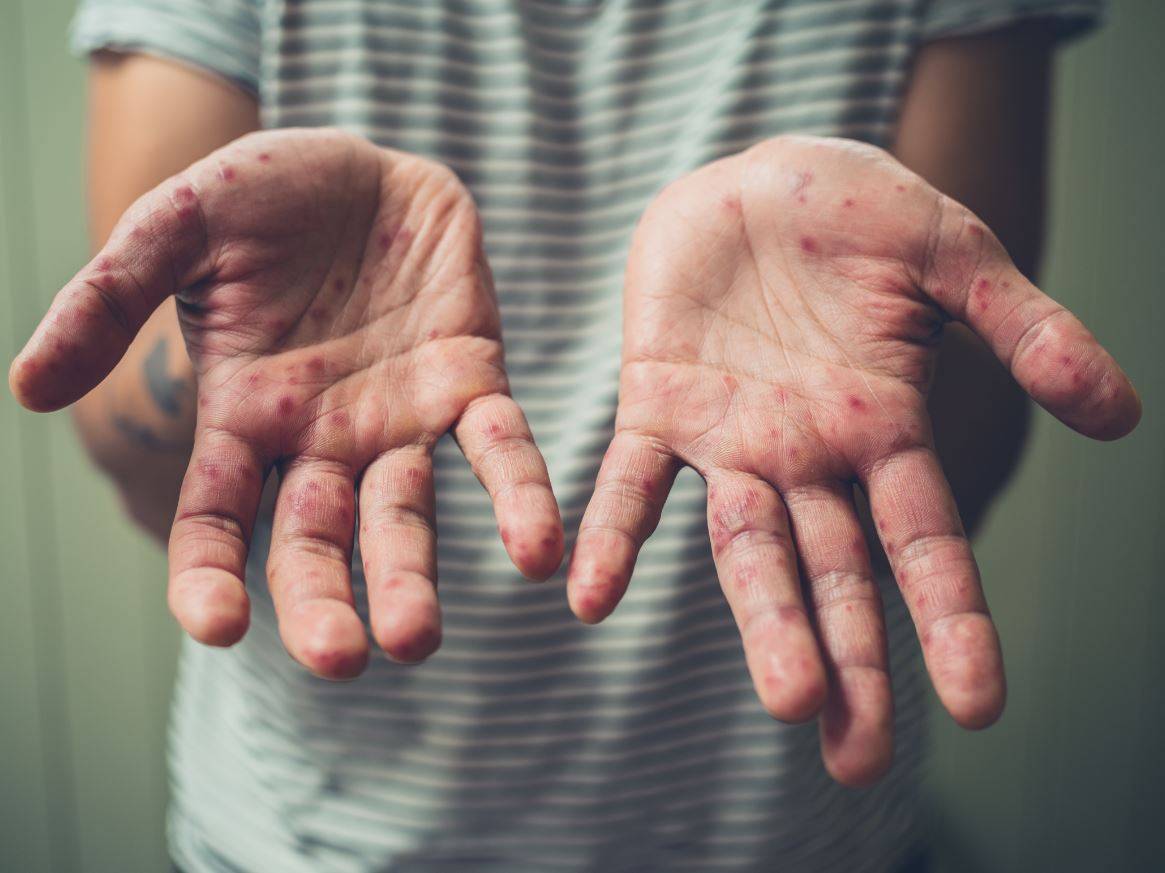
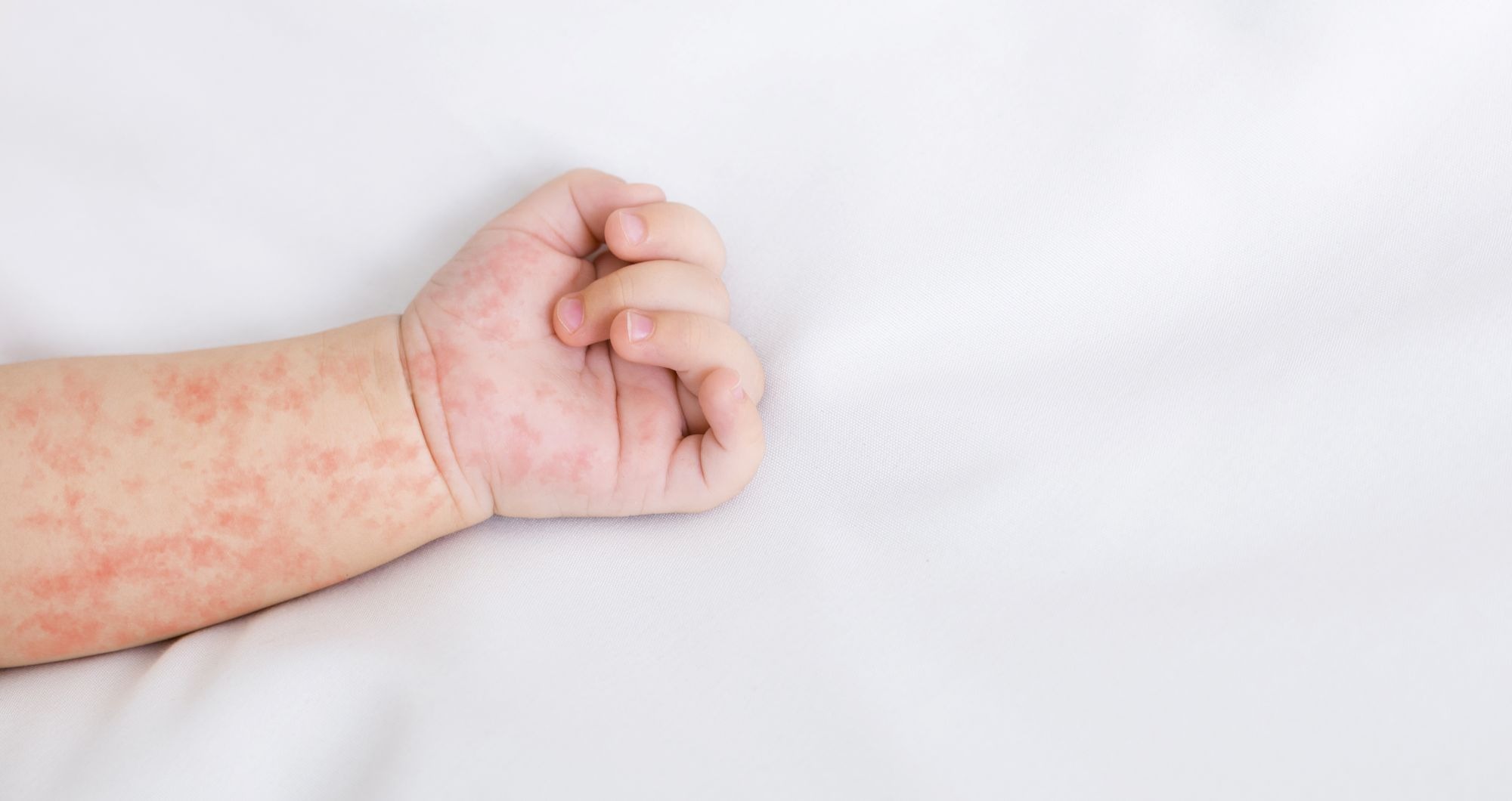
Measles cases in Europe and Central Asia fell in 2025 compared with 2024, according to preliminary data reported by 53 countries in the World Health Organization (WHO) European Region. This decline aligns with the preliminary figures published this week by the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). According to the WHO, countries in Europe and Central Asia reported 33,998 measles cases in 2025, representing a decrease of nearly 75 % compared with the 127,412 cases recorded in 2024. In Spain, however, the number of cases has increased, as shown by data from the Carlos III Health Institute. A few weeks ago, the WHO announced that Spain had lost its measles-free status.