Spanish National Research Council (CSIC)
If you are the contact person for this centre and you wish to make any changes, please contact us.
'Ramón y Cajal' postdoctoral researcher at the Biologial Mission of Galicia and head of the ECOP research group – Landscape Ecology
Senior Scientist at the Spanish Institute of Oceanography, IEO-CSIC
Virologist (senior scientist) at the Animal Health Research Centre (CISA, INIA-CSIC)
Researcher at the Instituto Cajal, CSIC
Doctor in Ecology and postdoctoral researcher at the National Museum of Natural Sciences (CSIC) in Madrid
Professor of Economics at Durham University (United Kingdom), Research Professor at the Spanish National Research Council (CSIC) and Lead Author of the International Cooperation chapter of the IPCC's AR6
Research professor at public research organisations at the CSIC Institute of History, in the Department of Archaeology and Social Processes
Researcher at the Institute of Public Goods and Policies of the CSIC (IPP-CSIC)
CSIC research professor and expert in food safety and water quality
Head of the Epidemiology and Environmental Health research group at CISA, INIA-CSIC.

A team from the United States has used data from health studies to analyze the extent to which prestigious journals capture or ignore science considered influential. Their findings indicate that most of the most cited articles—thus considered most influential—are published in journals not ranked among the most prestigious. According to the study, approximately half of all researchers never publish in a journal with an impact factor above 15, which, according to certain evaluation systems, could exclude them from opportunities. However, overall, traditional journal-based measures may only recognize between 10% and 20% of influential work. The results are published in Plos Biology.

Restrictions on mobility and activity imposed during the covid-19 pandemic had an impact on the beaks of a species of bird, specifically the dark-eyed junco, which lived in urban areas of Los Angeles (USA). This is shown in a study published in the journal PNAS, which reveals how birds born during these lockdowns had beaks similar to their counterparts in the wild. With the return of human activity, the beak returned to its pre-pandemic shape. The authors argue that this change was mainly due to an adaptation to the food available, as the birds no longer had access to human food waste.

An international team has analyzed data from nearly 60 studies involving more than 48,000 children with different types of diets and compared the nutritional profile and various health parameters between those following vegan, lacto-ovo-vegetarian, and omnivorous diets. The results indicate that plant-based diets, if well-planned, can promote healthy growth with benefits such as a better cardiovascular profile and lower cholesterol levels. However, they may have difficulty achieving adequate levels of vitamins D and B12, calcium, iron, and zinc. According to the authors, the findings underscore the need for careful planning and supplementation in children following these types of diets. The study is published in Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition.

The rapid growth of satellite constellations threatens the operation of space telescopes, according to a study published in Nature. If the planned launches are completed, the Hubble Space Telescope could see more than a third of its images affected by light pollution from these satellites, as they share the same orbital space, while other telescopes would have more than 96% of their images damaged, the authors estimate.

The veterinary services of the Catalan Regional Government have notified the Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries, and Food of the detection of two wild boars positive for African swine fever virus in Bellaterra (Barcelona), where they were found dead on November 26. These cases represent the first detection of the disease in Spain since November 1994, according to the ministry in a press release. African swine fever is considered a Category A disease by the European Union, which means that member states must take measures to control and eradicate it as soon as possible. It is a non-zoonotic disease, meaning that humans are not susceptible to infection either through contact with animals or through the consumption of animal products.

Viruses that cause avian influenza are capable of replicating at temperatures higher than a typical fever, according to a study in in vitro models and mice. ‘Fever-resistant replication could help explain why avian viruses and pandemic influenza viruses with avian PB1 cause more severe disease in humans,’ the authors write in the journal Science.

Consuming up to four cups of coffee a day is associated with an increase in telomere length in people with severe mental disorders, such as schizophrenia or bipolar disorder. Telomere length is an indicator of cellular ageing and is shorter in people with these disorders, although the causes are not clearly understood. According to the study, published in BMJ Mental Health, the effect shown is comparable to ‘a biological age five years younger’ in coffee drinkers.
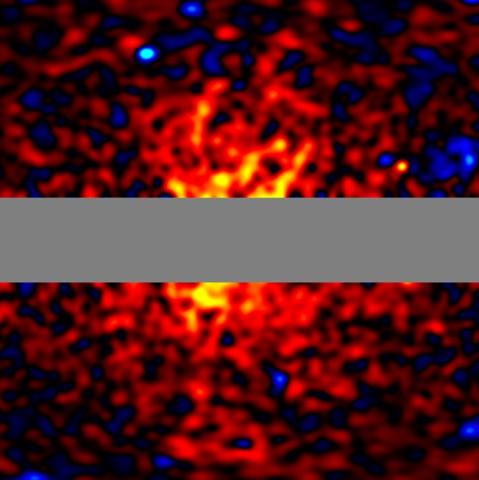
A century ago, astronomer Fritz Zwicky observed that galaxies were moving faster than their mass should allow, leading him to infer the presence of an invisible structure, dark matter. Since the particles that make up dark matter do not interact with electromagnetic force, they cannot be observed directly, as they do not absorb, reflect, or emit light. Now, NASA's Fermi space telescope has found specific gamma rays in the center of the Milky Way that are consistent with the decay of theoretical dark matter particles, although they could also come from other sources. “If this is correct, to my knowledge, it would be the first time that humanity has ‘seen’ dark matter,” said study author Tomonori Totani in a press release. The article is published in the Journal of Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics.

One day after the deadline, COP30 in Belém (Brazil) has finally reached a minimal agreement. The text does not mention a roadmap for abandoning fossil fuels, as requested by more than 80 states, including the European Union. The agreement states that countries agreed to accelerate climate action and triple funding for developing countries facing extreme weather events.

A team at Google DeepMind has developed AlphaProof, an artificial intelligence system that learns to find formal proofs by training on millions of self-formulated problems. According to the authors, the system “substantially improves upon previous-generation results on historical problems from mathematical competitions.” Specifically, in the 2024 International Mathematical Olympiad (IMO) for secondary school students, “this performance, achieved after several days of computation, resulted in a score equivalent to that of a silver medalist, marking the first time an AI system has achieved medal-level performance.” The results are published in the journal Nature.