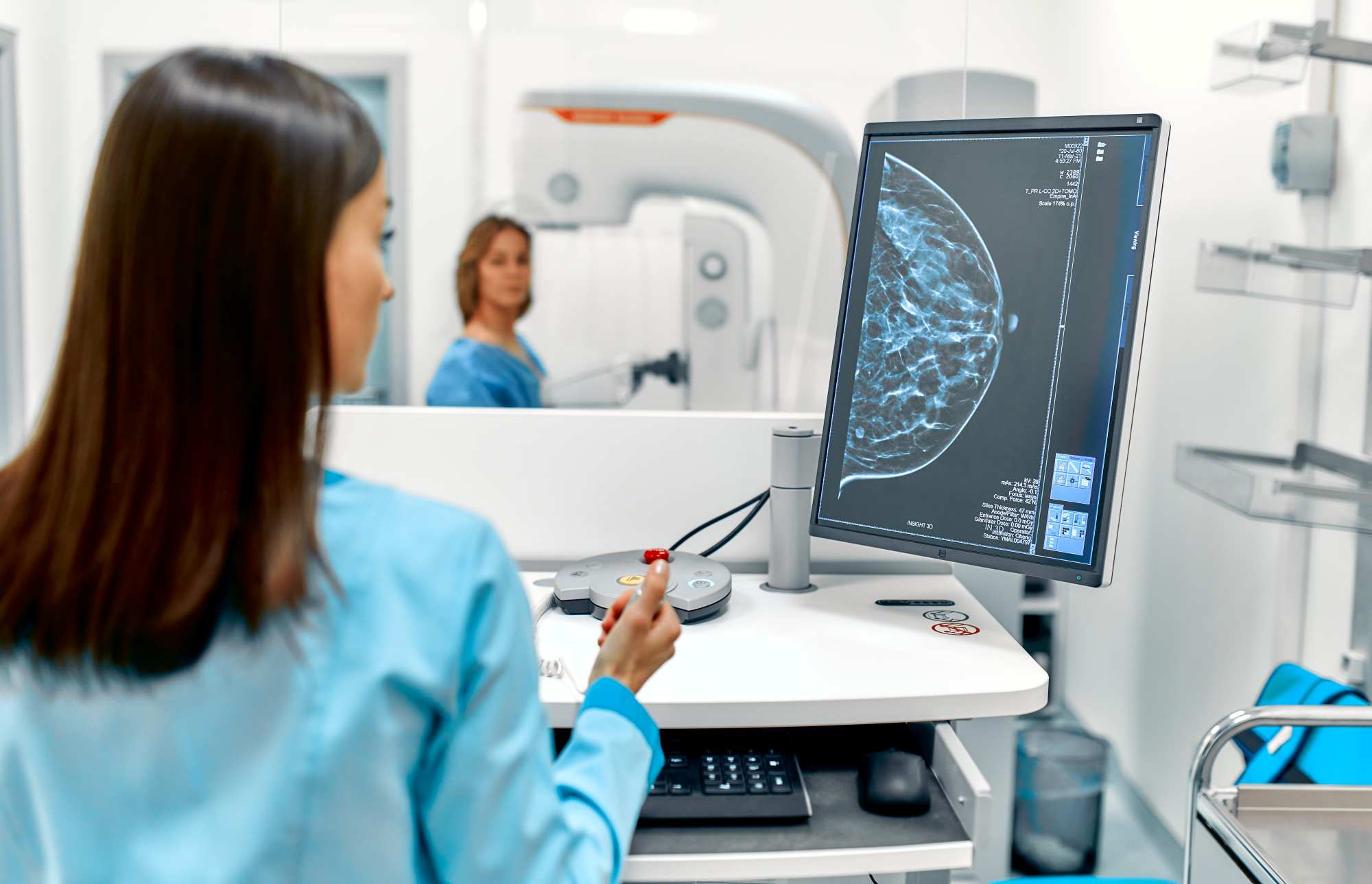
A clinical trial involving more than 100,000 women shows that AI improves breast cancer screening
Between April 2021 and December 2022, more than 100,000 women in Sweden were randomly assigned to either AI-assisted mammography screening or double reading, where two radiologists review each mammogram without the aid of AI. AI-assisted screening identified more women with significant cancers without a higher rate of false positives and also achieved a 12% reduction in the rate of interval cancers—those that appear between mammograms because they went unnoticed or are newly developed and more aggressive—compared to the double reading procedure. This is the first clinical trial of its kind, and its results are published in The Lancet.