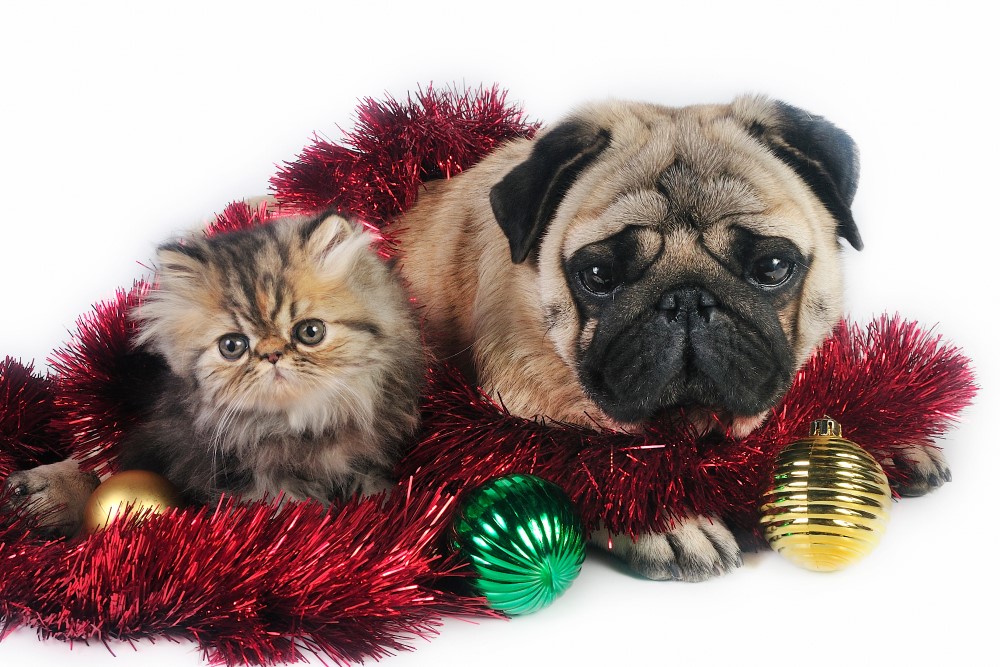
Some dogs and cats have been bred to have the same flat face
An analysis carried out in the United States has shown that, through intensive breeding and artificial selection, humans have pushed breeds such as pugs and Persian cats to evolve with very similar skulls and flattened faces. These two species, which have a common ancestor but have been evolutionarily separated for 50 million years, have converged to the point where they resemble each other more than they do members of their own species or their ancestors. According to the study, published in PNAS, ‘this phenomenon has not been observed before in domesticated species.’ The authors lament that humans ‘have bred brachycephalic breeds to such an extreme that they are prone to respiratory, feeding and birthing problems and would not survive in the wild.’