
The devastating floods in Valencia in October 2024 and the rainfall alert issued on September 28, 2025, showed that the way we communicate risks can make a difference, for better or for worse. This article presents eight key points for journalists, public officials, communicators, and anyone else interested in communicating better about floods and other crises.

The North American strain of the H5N1 avian influenza virus has been shown to be capable of causing outbreaks in mammals such as cows, something not seen elsewhere in the world, including Europe. An international team has identified and tested two mutations in ferrets that may explain improved adaptation and greater virulence. According to the authors, who published the results in the journal Science Advances, the finding "highlights the urgent need for strengthened surveillance and targeted interventions.

Through surveys of 78 healthcare workers in Gaza between August 2024 and February 2025, an international team has documented patterns of injuries among the civilian population during Israel's ongoing invasion. The most common traumatic injuries were burns, followed by injuries to the lower and upper limbs. Explosion damage accounted for most of the weapon-related trauma, which particularly affected the head, while gunshot wounds were mainly located in the lower limbs. The study is published in The BMJ.

An international team has analysed cancer incidence and mortality worldwide using data available since 1990. Between then and 2023, there was an increase of almost 75% in deaths from this cause, with more than 40% of all deaths associated with preventable risk factors. Estimates indicate that by 2050 there will be a similar increase in mortality, due in part to the ageing of the population. The increase will be particularly pronounced in low- and middle-income countries. The results are published in The Lancet.

Menstrual cycles were synchronised with lunar cycles until 2010, but according to research published in Science Advances, after this date, this synchrony is only found in January, when lunar gravity is at its strongest. The team analysed the menstrual records of 176 women and attributes the loss of synchrony to the increasing use of smartphones and LED night lights, which became widespread from 2010 onwards.

Maria Branyas was considered the oldest person in the world when she died in 2024 at the age of 117. An international team led by the Cancer Epigenetics group at the Josep Carreras Leukaemia Research Institute and the University of Barcelona has analysed her molecular profile, including her genome, metabolome, microbiome and epigenome. "Our results have helped us identify factors that could help many older people live longer, healthier lives," say the researchers, whose work is published in the journal Cell Reports Medicine.

At a press conference at the White House on Monday, Donald Trump and health authorities linked the use of paracetamol during pregnancy to cases of autism. They also recommended leucovorin as a treatment for autism. Immediately afterwards, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) announced in a press release that it had begun the approval process for calcium leucovorin tablets for patients with cerebral folate deficiency. “People with cerebral folate deficiency have been observed to have developmental delays with autistic characteristics, seizures, and movement and coordination problems,” they said. The update on the use of the drug, discussed by the scientific community, will authorize the treatment of children with autism spectrum disorder.

A study has estimated that there were more than 62,700 heat-related deaths in Europe between 1 June and 30 September 2024. This figure was 24% higher than that recorded in the summer of 2023, when more than 50,700 people died from heat, although 8.1% lower than in 2022, when more than 67,800 people died from this cause. By country, Spain had the second highest estimated mortality in the summer of 2024, with more than 6,700 deaths. The study, published in Nature Medicine and led by ISGlobal, proposes a new early warning system that can predict heat-related health emergencies at least one week in advance.

On Monday, US federal health authorities will advise pregnant women against taking paracetamol in the early stages of pregnancy, unless they have a fever, as reported yesterday by The Washington Post. The announcement will be accompanied by a recommendation for a drug called leucovorin as a treatment for autism, the article adds. Donald Trump said yesterday: ‘Tomorrow we are going to have one of the most important announcements... from a medical standpoint, I think, in the history of our country. I think we have found an answer to autism.’
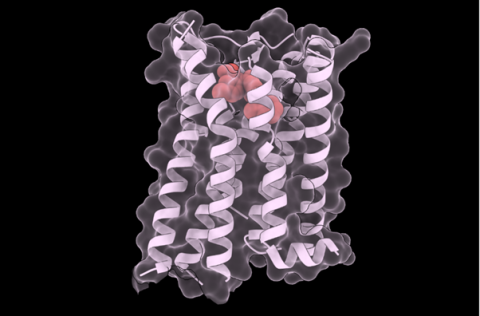
Most rare diseases are caused by mutations in DNA, but the same gene can mutate in different ways, which complicates treatment. Now, a team from the CRG in Barcelona has shown that an already approved drug is capable of stabilising almost all mutated versions of a human protein—specifically, the vasopressin V2 receptor, which is linked to a rare disease called nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. According to the researchers, who published their findings in Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, the study is the first proof of concept demonstrating that a drug can act as a ‘near-universal’ treatment, which could accelerate the development of therapies.