
On Monday, US federal health authorities will advise pregnant women against taking paracetamol in the early stages of pregnancy, unless they have a fever, as reported yesterday by The Washington Post. The announcement will be accompanied by a recommendation for a drug called leucovorin as a treatment for autism, the article adds. Donald Trump said yesterday: ‘Tomorrow we are going to have one of the most important announcements... from a medical standpoint, I think, in the history of our country. I think we have found an answer to autism.’
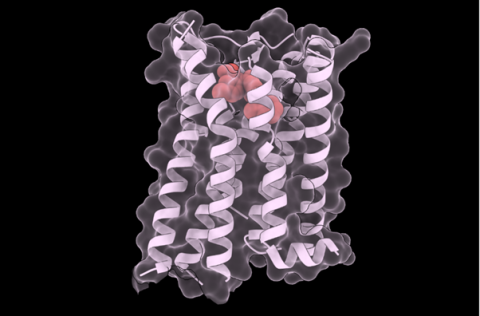
Most rare diseases are caused by mutations in DNA, but the same gene can mutate in different ways, which complicates treatment. Now, a team from the CRG in Barcelona has shown that an already approved drug is capable of stabilising almost all mutated versions of a human protein—specifically, the vasopressin V2 receptor, which is linked to a rare disease called nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. According to the researchers, who published their findings in Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, the study is the first proof of concept demonstrating that a drug can act as a ‘near-universal’ treatment, which could accelerate the development of therapies.

A new school year has begun, and pollution, which exceeds recommended limits in many urban centres, will once again affect children and their families. What consequences could this have on health? How does climate change affect it? What solutions can be implemented? SMC Spain organised an informative session with Julio Díaz and Cristina Linares to answer these questions.

Premature deaths due to smoke pollution from wildfires will multiply to reach nearly 1.5 million deaths per year by the end of the century, according to a study published in Nature. The authors estimate that the increase will be much greater in Africa (11 times more deaths in 2095-2099 than in 2010-2014) than in Europe and the US (up to twice as many). Another study published in the same journal estimates that, under a high CO2 emissions scenario, there will be more than 70,000 additional deaths per year from fires in the United States by 2050.

Avian influenza has returned to Spain this summer. In addition to a few cases in wild birds, since 18 July there have been several outbreaks in poultry in different autonomous communities, causing the country to lose its disease-free status. To answer questions about the situation, its possible causes, evolution and consequences, SMC Spain organised an information session with researchers Inmaculada Casas, Ursula Höfle and Elisa Pérez Ramírez.
In an analysis published by The Lancet Global Health, a panel of specialists urges the medical community to recognize type 5 diabetes as a disease distinct from other types of diabetes. This form of the disease —first described in 1955 and whose name “type 5” was recognized by the International Diabetes Federation in April 2025— affects 25 million people with a low body mass index, mainly in low- and middle-income countries, according to the authors' estimates. People with type 5 diabetes do not produce enough insulin, but their bodies process insulin normally. In addition, they do not usually suffer from ketoacidosis —an acute metabolic complication of diabetes— and their immune systems do not attack the pancreas.

Antiretroviral therapy has become a vital treatment for people with HIV. However, it is not a cure, because the virus is able to take refuge and hide in certain blood cells. Now, a study of 65 people—30 women and 35 men—who were undergoing this therapy has found that women's immune systems tend to be more effective at controlling the virus. According to the researchers, who published their findings in the journal Science Translational Medicine, the study ‘reinforces the importance of considering sex in the design and implementation of medical interventions aimed at cure and suggests that women may be better candidates for exploring innate immunity-dependent strategies.’

An artificial intelligence (AI) tool can predict the probability of more than 1,000 diseases based on a person's medical history, with greater accuracy than existing technologies, which focus on fewer pathologies, according to the authors in Nature. This model, called Delphi-2M, is also capable of simulating health trajectories for up to 20 years. The tool was trained with health data from 400,000 people in the United Kingdom and tested using data from nearly two million people in Denmark.

If the United States did not change the time twice a year, there would be a lower incidence of obesity and strokes. This is the conclusion of a study by Stanford University (USA) published in PNAS that compared how three different time policies — permanent standard time (winter), permanent daylight saving time, and biannual time changes — could affect circadian rhythms and the health of the population. By modelling light exposure, circadian impacts and health characteristics county by county, the researchers estimate that permanent standard time would prevent about 300,000 cases of stroke per year and reduce the number of people with obesity by 2.6 million, compared to biannual changes. Permanent daylight saving time would also be positive, although with a smaller impact.
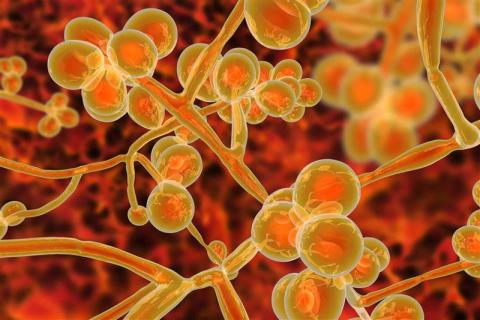
Infections caused by the fungus Candidozyma auris—formerly known as Candida auris—continue to rise, warns a report by the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). Spain reported 1,807 of the 4,012 cases in 36 European countries between 2013 and 2023, the highest number ahead of Greece (852 cases) and Italy (712), according to the survey. This microorganism spreads particularly in hospitals, causing infections that are often resistant to existing drugs.