
Artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted protein engineering is enabling advances in the design of new molecules, but it also poses biosafety challenges related to the potential production of harmful or dangerous proteins. Some of these threats, whether deliberate or accidental, may not be detected by current control tools. An international team has analyzed the situation and developed software patches to improve their identification, although they acknowledge that it remains incomplete. The authors of the study, published in the journal Science, warn that some of the data and code should not be published in a public repository due to its potential misuse.

The frequency of fire-related disasters increased significantly from 2015 onwards, according to a study analysing data from reinsurance companies between 1980 and 2023. Forty-three per cent of the 200 most damaging events, in terms of both human and economic damage, occurred in the last decade, the authors estimate in the journal Science. The risks were highest in the Mediterranean and in temperate coniferous biomes, and their frequency coincides with increasingly extreme weather conditions, they add.

Puppies that suffer traumatic experiences are more likely to be fearful or aggressive in adulthood, according to a study published in Scientific Reports. The analysis is based on data from nearly 4,500 dogs whose owners completed a canine behaviour assessment questionnaire. The authors analysed correlations between behaviours, such as biting or retreating, and early experiences of abuse or neglect, and found that some breeds are more resilient and others more vulnerable.
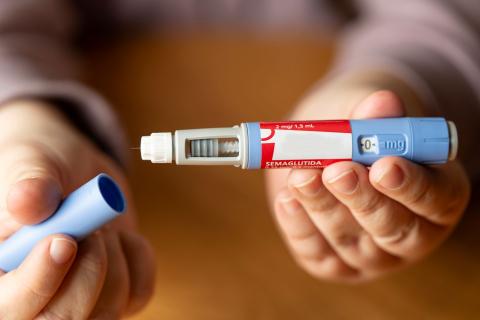
An article published in Nature Medicine outlines the new framework for pharmacologically treating obesity and its complications established by the European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO). The new guidelines establish semaglutide and tirzepatide as first-line treatment for this disease and most associated conditions. The team of authors, with Spanish participation, reviewed the scientific evidence on the effects of drugs on total weight loss and its complications and designed an algorithm to help medical personnel guide treatment, taking into account each patient's medical history and the action profiles of available medications.

English ethologist Jane Goodall died on Wednesday at the age of 91 in California (United States), where she was participating in a lecture tour. This was announced by the Jane Goodall Institute on its social media. ‘Dr Goodall's discoveries as an ethologist revolutionised science and she was a tireless advocate for the protection and restoration of our natural world,’ the statement said. Her observations and analysis of chimpanzees in the wild over decades were a milestone in primatology.

People with autism have different genetic and developmental profiles depending on the age at which they were diagnosed, according to a study published in Nature. The authors distinguish two groups: the first receive a diagnosis of autism in early childhood, with lower social and communication skills and a moderate correlation with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and mental health disorders. The other group of people receive their diagnosis in adolescence, with increased socio-emotional and behavioural difficulties, and higher genetic correlations with ADHD and mental health disorders.
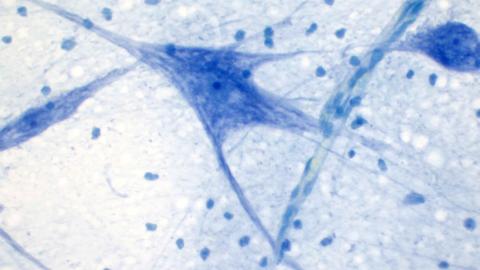
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a neurodegenerative disease characterised by progressive loss of motor neurons. An international team has discovered evidence that ALS may have an autoimmune component, meaning that the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells, a hypothesis that had been considered by the scientific community. The study shows that inflammatory immune cells—called CD4+ T cells—attack certain proteins that are part of the nervous system in people with ALS. ‘These findings highlight the potential of therapeutic strategies aimed at improving regulatory T cells,’ the authors note in the research, published in Nature.
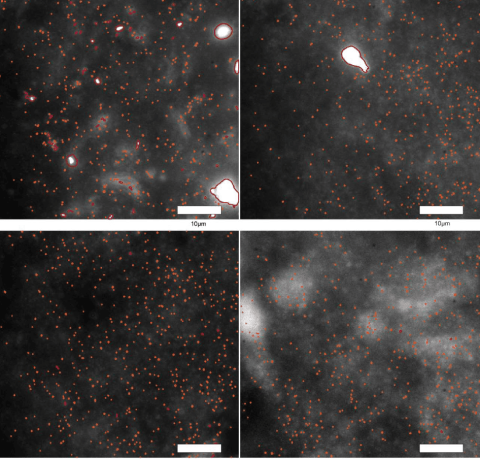
A team has managed to visualise and quantify the protein aggregates believed to trigger Parkinson's disease. This is the first time they have been directly visualised. These small aggregates – alpha-synuclein oligomers – were observed in post mortem brain tissue from people with the disease using a new microscopy technique, as explained by the authors in Nature Biomedical Engineering.
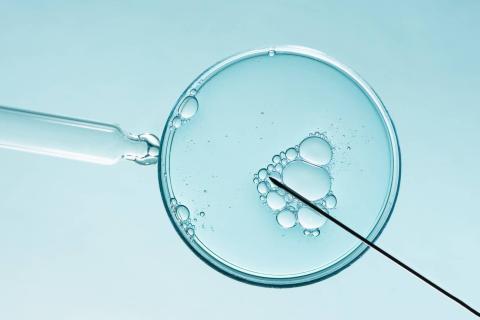
An international team has succeeded in generating fertilisable human eggs from skin cells using a novel technique. According to the authors, the study offers a way to address infertility, although they acknowledge that further research is needed to ensure efficacy and safety before future clinical applications. Of the 82 functional oocytes generated and fertilised, only 9% developed to day 6, when the experiment ended. In addition, the embryos had chromosomal abnormalities. The results are published in the journal Nature Communications.
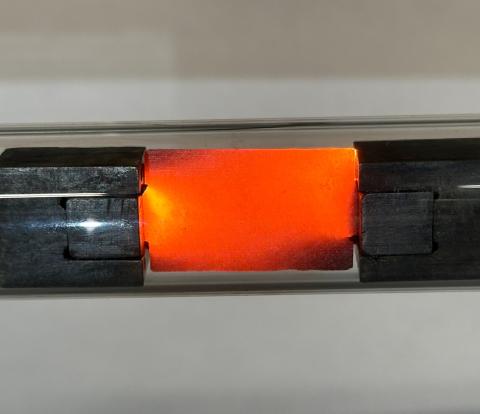
A US research team has designed an ‘environmentally friendly and economically viable’ method for recovering rare earth elements from electronic waste. It is cheaper than traditional methods, uses less water, acid and energy, and emits fewer greenhouse gases, according to the authors in PNAS. Rare earth elements (REE) are a group of chemical elements needed to manufacture batteries, magnets and electronic components. Both the European Union and Spain are committed to these critical materials in order to reduce their dependence on foreign sources.