
Funding has been one of the major obstacles to agreement at the Baku Climate Summit. More sustainable science also depends on how research is funded. It is imperative that research institutions also develop strategies to incorporate more sustainable practices and contribute to climate neutrality.

En un parque nacional del norte de la India, una investigación ha revelado que hay hombres que usan las tecnologías de vigilancia de la fauna para observar a mujeres sin su consentimiento e intimidarlas. El estudio, realizado por la Universidad de Cambridge (Reino Unido), describe cómo individuos de pueblos cercanos al bosque y de gobiernos locales hacen un mal uso de cámaras, grabadoras de sonido y drones, originalmente destinados a vigilar áreas protegidas con fines de conservación de animales. Esas tecnologías “son fácilmente captadas para fines ajenos a la conservación que refuerzan normas patriarcales y propagan la violencia estructural de género”, denuncia la investigación, que se publica en Environment and Planning F.

In the early hours of the morning, after more than two weeks of negotiations and on the verge of collapse, participants at COP29 in Baku (Azerbaijan) reached an agreement to set the new climate finance target. In the end, at least 300 billion dollars a year will be contributed by rich countries to the least developed countries until 2035, within a broader global commitment of up to 1.3 trillion dollars directed at these same countries. The renewal of this target was part of the Paris Agreement and will enable governments to support developing countries in their climate action on adaptation, mitigation and damage from the climate crisis. The previous target - set at the Copenhagen Summit in 2009 - was $100 billion per year.
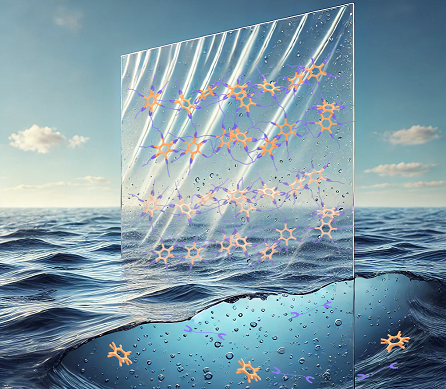
A study published today in Science reveals a new plastic as durable as conventional plastics that decomposes in seawater. According to the authors, this new material could help reduce microplastic pollution accumulating in the oceans and eventually entering the food chain.

A US study analysed data from more than 110,000 women since 1993 and found that those with a history of endometriosis had a 31% higher risk of premature death (before the age of 70). In absolute terms, the rate of premature death in women with and without endometriosis was 2 and 1.4 per 1,000 person-years, respectively. In contrast, the presence of uterine fibroids was not associated with an overall increased risk, although the risk of death from gynaecological tumours was increased. The results are published in The BMJ.
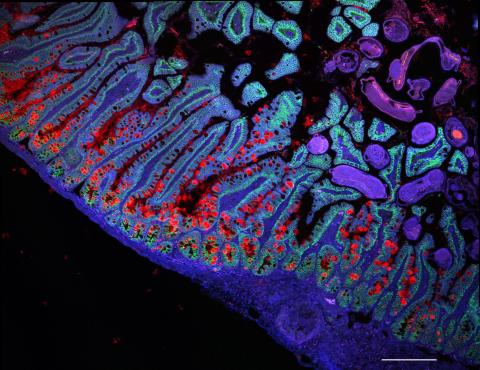
The Human Cell Atlas, an international research consortium, publishes biological data from different cell types in the human body in a series of articles in Nature and other journals in its family. One of the articles integrates single-cell RNA sequencing datasets from the gastrointestinal tract of healthy people and others with different diseases. It describes inflammation-induced changes in stem cells that alter mucosal tissue architecture and promote increased inflammation, a concept that can be applied to other tissues and diseases.

Adipose tissue retains a ‘memory’ of obesity through cellular transcriptional and epigenetic changes that persist after weight loss, which may increase the likelihood of regaining weight, experiments in human and mouse cells show. The findings, published in Nature, could help explain the problematic ‘yo-yo effect’, the rapid weight rebound often seen with dieting.

The DANA that devastated the province of Valencia on 29 October, leaving more than 200 people dead and many missing, has been followed by another one, still located over the peninsula. How can we adapt to these extreme phenomena? What repercussions do they have on public health? How can the public prepare for them? The Science Media Centre España organised a briefing session with two experts and an expert from the CSIC to discuss these questions.

Adults make better decisions than adolescents, according to a study of 92 participants aged 12 to 42. So-called ‘noise’ in decision-making - making choices that are not the most efficient - decreases with age and is linked to the development of skills such as flexibility and planning, according to the study published in PLoS Biology.

If practices and public policies do not change, the mass of mismanaged plastic waste in the world will double to 121 million tonnes per year by 2050, according to a study published in Science. The article also assesses the potential impact of global measures, such as those envisaged by the forthcoming UN global treaty on plastic pollution, which begins its final negotiating session at the end of this month.