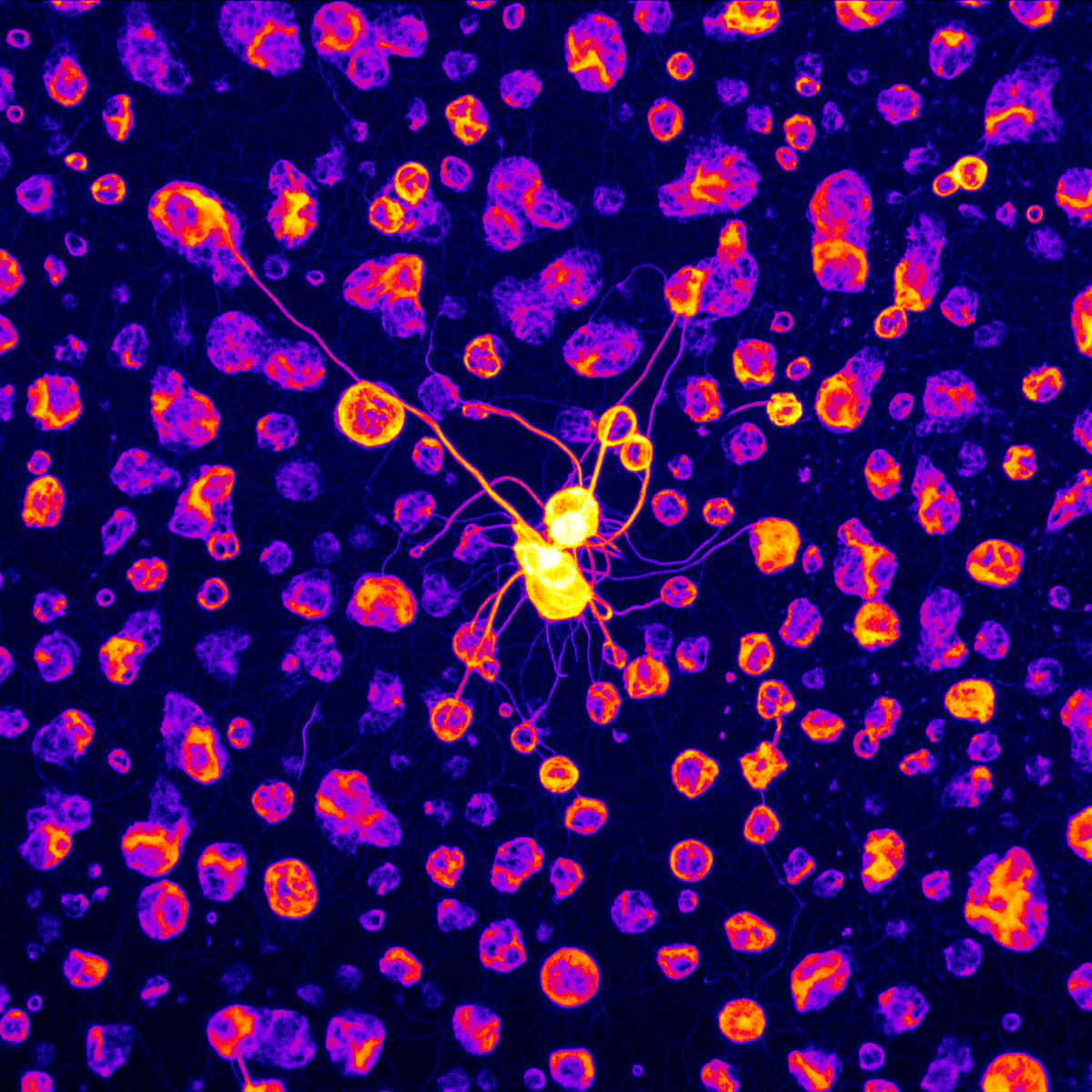
Evidence found that ALS may have an autoimmune component
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a neurodegenerative disease characterised by progressive loss of motor neurons. An international team has discovered evidence that ALS may have an autoimmune component, meaning that the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells, a hypothesis that had been considered by the scientific community. The study shows that inflammatory immune cells—called CD4+ T cells—attack certain proteins that are part of the nervous system in people with ALS. ‘These findings highlight the potential of therapeutic strategies aimed at improving regulatory T cells,’ the authors note in the research, published in Nature.