A phase 3 clinical trial has tested a new RNA vaccine against influenza
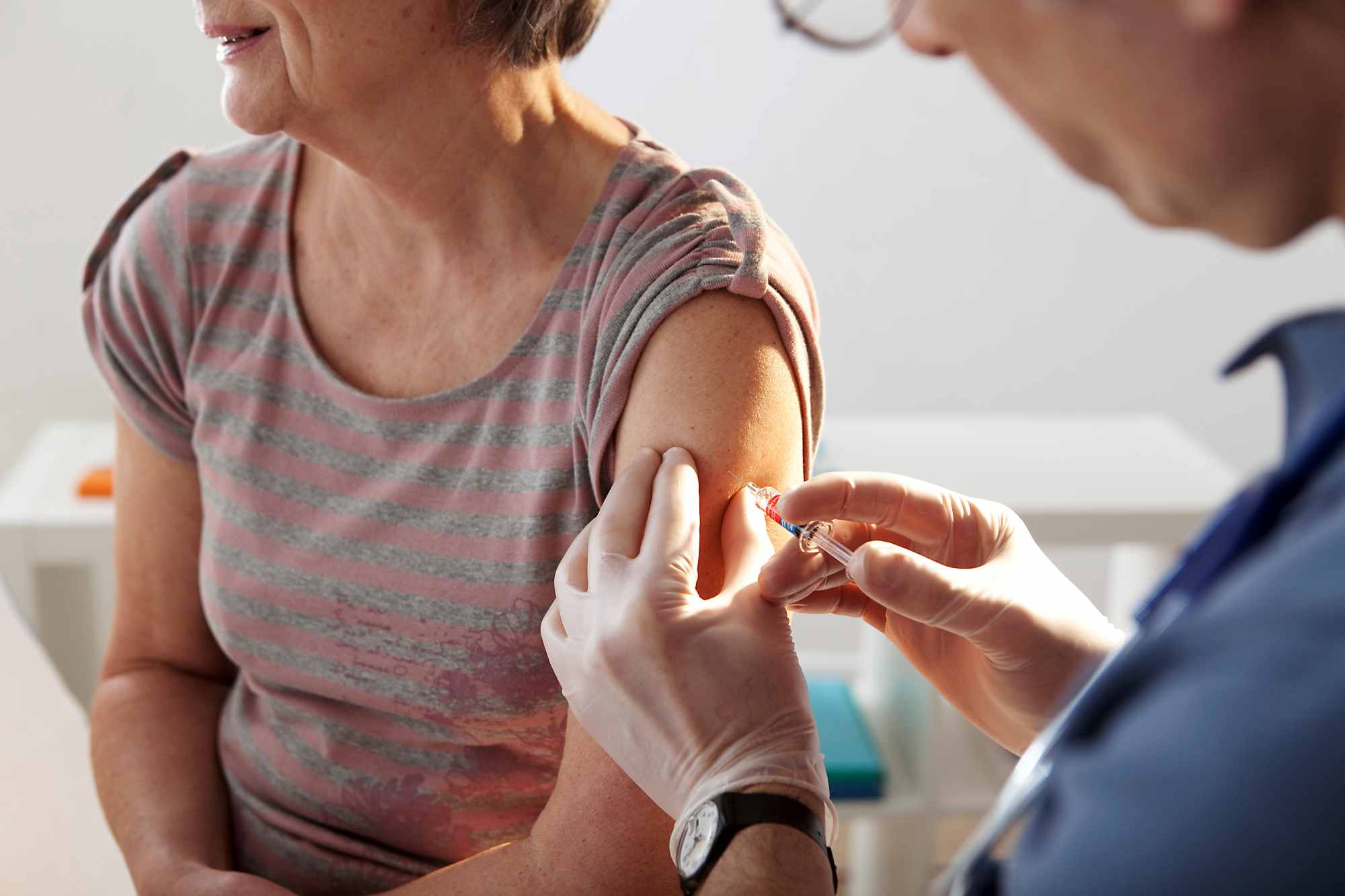
A clinical trial funded by Pfizer has tested a new influenza vaccine based on messenger RNA (mRNA). The phase 3 trial included more than 18,000 people aged 18 to 64, half of whom received the new compound and the other half a conventional vaccine. The results indicate that the mRNA vaccine was more effective, but it also caused more adverse reactions: for example, 5.6% of the volunteers who received it developed a fever, compared to 1.7% of those who received the conventional vaccine. The study is published in the journal NEJM.