
A systematic review published in BMJ Global Health that includes an analysis of 31 studies concludes that the method known as 'skin-to-skin' - or 'kangaroo care' - used with premature or low-weight babies can reduce the risk of mortality by 32% and the risk of serious infections by 15%. The research, funded by the World Health Organisation, shows that starting the technique within 24 hours of birth and carrying it out for at least eight hours a day increases its effectiveness.
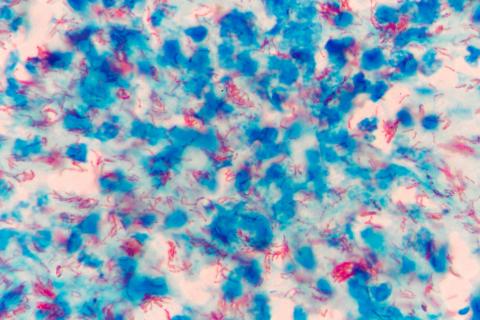
The Regional Ministry of Health of the Xunta of Galicia reported a few days ago that it had detected a case of tuberculosis in a high school in Ourense. Yesterday it confirmed that it is following up the contacts of the case after 19 positive tuberculin tests were detected, which implies contact with the bacteria but not necessarily the development of the disease.

A study based on data from the Environmental Justice Atlas says that 81 women were murdered worldwide for their environmental activism: one of them in Spain, 7 in Colombia, 5 in Honduras and 4 in Peru, among other countries. The study, published in Nature Sustainability, says that violence against women defenders is concentrated in conflicts around mining, agribusiness and industrial projects in the Global South. The first author of the study is Dalena Tran, a researcher at the Institute of Environmental Science and Technology of the Autonomous University of Barcelona.

A special issue published in the journals Science and Science Advances shares for the first time the genomes of hundreds of primates, representing 86% of known genera. One of the papers -co-led by the Institute of Evolutionary Biology and the Pompeu Fabra University- analyzes the relationship between the genes of these animals and the risk of suffering from certain diseases such as cancer in humans.
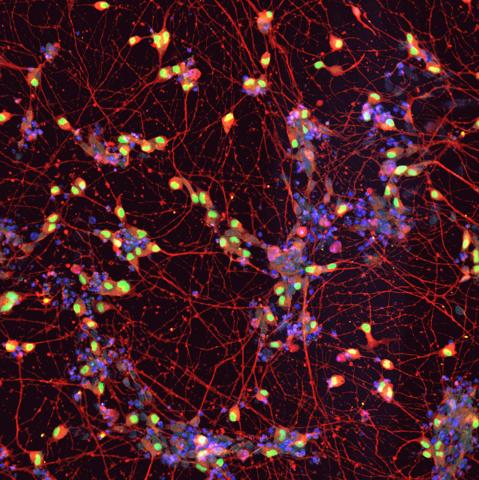
A research team in Japan has published a small clinical trial in 20 people with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) of a drug called ropinirole, which is commonly used in patients with Parkinson's disease. The authors, whose study is published in Cell Stem Cell, say the treatment is safe and slowed the progression of ALS - an incurable neurodegenerative disease - by an average of 27.9 weeks.

A team of scientists led by the Catholic University of America in Washington has designed new artificial vectors based on viruses to improve gene therapy processes. The main novelty is that they are constructed from viruses that infect bacteria. Among other advantages, this would make it possible to avoid the possible memory of our defences against them and have a greater capacity. According to the authors, who publish their results in the journal Nature Communications, these nanoparticles "have the potential to transform gene therapies and personalised medicine".

An international team of scientists, led by Stanford University (United States), has designed a study to analyse the relationship between herpes zoster virus infections and the development of dementia. To do so, they took advantage of the introduction of the Zostavax vaccine against this virus in 2013 in Wales (UK), which people over the age of 80 could not receive. After reviewing data from people around this age over the following seven years, they concluded that the vaccine reduced the relative risk of dementia by 20%. According to the authors, their study, which is in prepublication form and has not been peer-reviewed, "leads to the conclusion that shingles vaccination is most likely an effective way to prevent or delay the onset of dementia".

A few weeks ago, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) said that exposure to bisphenol A through food is a risk to human health. The agency recommended a much lower tolerable daily intake dose than it had its own previous recommendations. In this explainer, we review key facts and documents to cover this issue--which will continue to make the headlines in months and years to come.

By directing ultrasound to a specific area of the brain, scientists at the University of Washington have succeeded in inducing a state very similar to hibernation in rats and mice. This state, called "torpor", involves a reduction in metabolism and body temperature to save energy. According to the authors, who publish their results in the journal Nature Metabolism, if it could be applied to humans it could be used in space travel or in medicine, to increase the chances of survival in life-threatening situations such as heart attacks or strokes.

A meta-analysis including 30 clinical trials published between 1980 and 2022 concludes that vegetarian and vegan diets are associated with lower blood lipid concentrations, including cholesterol. The research is published in the European Heart Journal.