
The last few weeks have been marked by devastating fires in Spain and other European countries. In Catalonia, just days after a fire killed two people and burned 5,500 hectares in the province of Lleida, another fire broke out in the province of Tarragona, affecting more than 3,200 hectares and now stabilised, which resulted in another person's death. What are the characteristics of these large fires? How can we prevent them? The Science Media Centre Spain organised an informative meeting with two experts to answer these questions and clarify key concepts.

Most research on the presence of plastics in the seas has focused on macro- and microplastics. Now, an international team has analyzed the presence of nanoplastics - smaller in size - in different locations and depths of the North Atlantic Ocean, including areas near the European coasts. The results suggest that these may account for the majority fraction of the total mass of plastic in the oceans and that the total mass of marine plastic may be greater than previously thought. The work is published in the journal Nature.
An international team has studied dominance relationships between the sexes in 253 populations of 121 different primate species. The data collected indicate that clear dominance by one sex or the other is rare, despite the fact that it was long believed that males dominated females socially in most of them. According to the press release accompanying the paper, the work “challenges traditional views on the natural origins of gender roles.” The results are published in the journal PNAS.
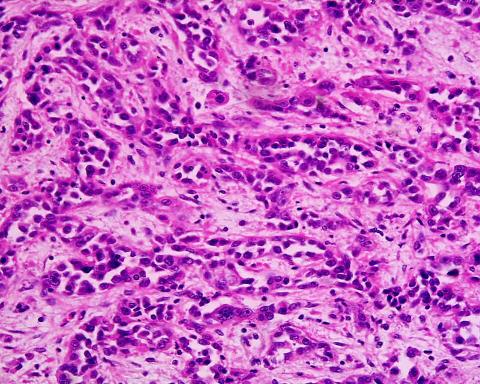
Research estimates that 15.6 million people born between 2008 and 2017 worldwide will develop gastric cancer at some point in their lives if current trends continue. In Spain, there would be 58,641 cases, or 1.24% of people in this age group. The team used data on gastric cancer from 185 countries in 2022 combined with mortality projections based on United Nations demographic data. The estimates, published in the journal Nature Medicine, show that 76% of cases could be attributed to Helicobacter pylori, a common bacterium found in the stomach.
A US team has analysed the presence of beta-amyloid deposits – which are linked to Alzheimer's disease – in the post-mortem retinas of four people with covid-19 and found that they were larger than in four people without covid. In complementary experiments, the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in retinal organoids produced an increase in deposits, while the use of a drug that blocks the virus from binding to neurons reduced their accumulation. The results are published in the journal Science Advances.
A team from Sweden has analysed post mortem brain samples from people aged between 0 and 78 using various techniques and found that, although it varies between individuals, new neurons continue to form in the hippocampus with no apparent age limit. Although previous studies had reached similar conclusions, controversy remains about these results. According to the authors, the new work ‘provides an important piece of the puzzle in understanding how the human brain works and changes throughout life.’ The results are published in the journal Science.

US Department of Health Secretary Robert Kennedy Jr's proposal to let bird flu spread in turkeys and chickens to identify surviving animals would be "dangerous and unethical", a group of scientists warns in a policy forum article published by Science. In addition to the suffering of infected animals, allowing a highly lethal, rapidly evolving and contagious virus to follow a natural course of infection "would prolong exposure for farmworkers, which could increase viral adaptation and transmission risks for poultry, other peridomestic animals, and humans," they warn.

Two people have died in a fire that has burned more than 5,500 hectares in the province of Lleida. Firefighters from the Catalan government declared it under control last night, after 29 hours. Salvador Illa, president of the Catalan regional government, called for ‘maximum caution’ from the public, warning that ‘today's fires are not like those of the past, they are extremely dangerous,’ according to RTVE.es. Why is this fire considered extreme? What should you do when a fire breaks out? How can more fires be prevented? In this article, we have compiled explanations and basic recommendations with the help of expert sources.

The brain can become habituated to the deterioration of democracy, warn a neuroscientist and a law expert in an editorial published in Science Advances. "When democratic norms are violated repeatedly, people begin to adapt,’ they explain, calling for a "dishabituation" to democratic decline. This requires "see[ing] things not in light of the deterioration of recent years, but in light of our best historical practices, our largest ideals, and our highest aspirations.

Although tobacco consumption is declining in many parts of the world, there appears to be an increase in the number of lung cancer cases among non-smokers. One of the possible causes of this increase is air pollution. Now, researchers in the US, with Spanish participation, have analysed the genomes of 871 lung tumours in people from various locations who had never smoked. The results, published in the journal Nature, indicate that greater exposure to pollution is linked to an increase in the number of mutations, including those commonly associated with tobacco.