A research team from Murcia has found several types of microplastics in 69% of follicular fluid samples from 29 women and 55% of seminal fluid samples from 22 men, according to a presentation at the annual meeting of the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology (ESHRE), being held from 29 June to 2 July in Paris, France. The most frequent polymer in both types of samples was polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). The abstract of the research is published in the journal Human Reproduction.
An international study with 72 participants has found that greater connectivity between certain brain areas is associated with greater mathematical computational ability. In addition, weak electrical stimulation in a particular area was associated with improved computational learning in volunteers with lower connectivity. The results are published in the journal Plos Biology.

Aging is associated with an increase in chronic inflammation, a phenomenon known as inflammaging that is related to different diseases and that was considered universal. Now, an international team has analyzed data on 19 inflammation-associated proteins in four different populations: two industrialized (from Italy and Singapore) and two non-industrialized (the Tsimane population of the Bolivian Amazon and the Orang Asli population of Malaysia). The results show that, at least according to this form of measurement, in the non-industrialized populations there is no increase in inflammation with age, which questions whether this is a biological imperative and indicates that it would depend on lifestyles and social and cultural factors. The paper is published in letter format in Nature Aging.

From 2014 to 2023, one in six people in the world suffered from loneliness, according to a World Health Organisation report, which outlines the causes of this phenomenon and its multiple impacts: on physical and mental health and mortality, as well as on work and the economy. The report estimates that loneliness is linked to more than 871,000 deaths per year and highlights a higher incidence among young people and in low- and middle-income countries.

With the summer holidays approaching, questions arise about how to prepare for trips to other countries, including health recommendations. In this guide, we explain the basics of how to protect yourself and others.

Trump's measures are directly affecting trans and non-binary people in science. This uncomfortable mirror is not unique to the United States. International studies have documented how the LGTBIQA+ community in science experiences less safe working environments, greater discrimination and more frequent abandonment of academic careers. Better science will only be possible if it protects and celebrates all the people who make it possible.
An analysis published in the medical journal The BMJ points out that lifestyle changes recommended by doctors to people with obesity, focusing on calorie restriction and increased physical activity, have little effect on long-term weight loss, fail to significantly reduce cardiovascular risks and, yet, can lead to discrimination, stigmatisation and eating disorders. The authors also point out that weight alone is an inadequate measure of a person's health, as reflected in recent clinical guidelines, and propose a ‘health for all sizes’ approach with effective, patient-centred care.

Spanish citizens trust science and researchers, and want them to be more involved in the issues that affect people's lives. Television and social media are the most commonly used channels for obtaining information on these topics. 81.4% recognise that climate change is a serious problem and, with regard to AI, although more than 80% use it, there is concern about its risks and governance. These figures come from the latest edition of the FECYT's biennial Social Perception of Science and Technology Survey (EPSCT) 2024.
Between 1980 and 2023, childhood vaccination rates against diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, measles, polio and tuberculosis doubled worldwide, according to a study published in The Lancet. However, this increase slowed in many countries between 2010 and 2019; during this period, measles vaccination declined in half of all countries.
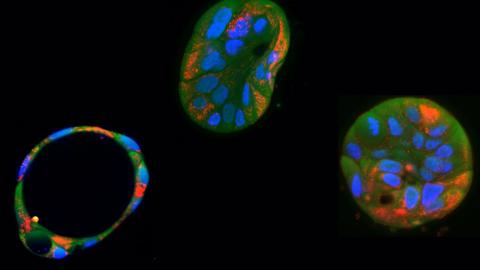
A team from the Netherlands has successfully edited pathogenic mutations in mitochondrial DNA in human cells, changes in DNA that cause disease, according to research published in PLoS Biology. The authors used a genetic tool known as a base editor. Until now, techniques derived from CRISPR have made it possible to correct mutations in nuclear DNA, and new techniques are being developed that allow mitochondrial DNA to be edited.