University of Valencia
If you are the contact person for this centre and you wish to make any changes, please contact us.
Associate Professor of Oncology, Faculty of Medicine and Dentistry, University of Valencia; Chief Physician of the Medical Oncology Department, Valencia University General Hospital Consortium
Professor of the Department of Statistics and Operations Research at the University of Valencia
Professor of Genetics at the University of Valencia and researcher of the Genomics and Health Area at the Foundation for the Promotion of Health and Biomedical Research of the Valencian Community (Fisabio)
Professor of Obstetrics and Gynaecology in the Department of Paediatrics, Obstetrics and Gynaecology
Professor of Theoretical Physics at the Institute of Corpuscular Physics (IFIC), University of Valencia - CSIC
Group Leader of the Functional Inorganic Materials Team (FuniMAT) at the Institute of Molecular Science (ICMol) and senior lecturer in the Department of Inorganic Chemistry at the University of Valencia.
Professor of Journalism and POLIBIENESTAR researcher at the University of Valencia
Researcher at the Climate, Atmosphere and Oceans Laboratory (Climatoc-Lab) at the Desertification Research Centre (CIDE, CSIC-UV-GVA)
Educational sociologist and lecturer in Sociology of Education at the University of Valencia
CIBEROBN researcher and professor at the University of Valencia

Adopting a healthy diet at age 45 can add between two and three years to life expectancy in men, and between 1.5 and 2.3 years in women, according to a study based on data from more than 103,000 people in the United Kingdom. The positive impact is greater for men who follow a diabetes risk reduction diet (DRRD) and for women who follow a Mediterranean-style diet (AMED), says the article published in Science Advances.

Various studies have shown that exercise benefits the brain. Now, an international team has studied in mice how physical activity affects the brain and how these changes influence the effects of exercise. The research, published in Neuron, has shown that physical activity causes brain changes in a region of the hypothalamus involved in how the body uses energy and in regulating blood sugar. If these neurons were blocked immediately after exercise, the animals showed no improvement in endurance or metabolism with training. The authors suggest that activating these neurons may help the body recover faster, allowing other parts, such as the muscles, lungs, and heart, to adapt more quickly to more intense workouts.

Science journal has published a global map showing exposure to perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) through the consumption of fish products. PFAS are substances that are difficult to break down, meaning they can accumulate in the body, and some are linked to health problems. The authors collected data over 20 years from PFAS measurements in the marine environment and fisheries, and mapped the concentrations of these compounds in more than 200 species of marine fish. The study shows that international fish trade redistributes the risk of PFAS exposure from highly polluted regions to less exposed areas, with European trade playing a key role in increasing the risk of exposure to these substances.

The prevalence—proportion of cases—of hypertension in minors has almost doubled worldwide between 2000 and 2020, rising from 3.4% to 6.53% in boys and slightly less in girls, according to a systematic review published in The Lancet Child & Adolescent Health. The study brings together data from nearly 444,000 children and adolescents up to the age of 19 in 21 countries.

The Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences has awarded the 2025 Nobel Prize in Chemistry to Susumu Kitagawa, Richard Robson, and Omar M. Yaghi for the development of molecular structures with large spaces through which gases and other chemicals can flow. These structures, called metal-organic frameworks, can be used to extract water from desert air, capture carbon dioxide, store toxic gases, or catalyze chemical reactions.

If the United States did not change the time twice a year, there would be a lower incidence of obesity and strokes. This is the conclusion of a study by Stanford University (USA) published in PNAS that compared how three different time policies — permanent standard time (winter), permanent daylight saving time, and biannual time changes — could affect circadian rhythms and the health of the population. By modelling light exposure, circadian impacts and health characteristics county by county, the researchers estimate that permanent standard time would prevent about 300,000 cases of stroke per year and reduce the number of people with obesity by 2.6 million, compared to biannual changes. Permanent daylight saving time would also be positive, although with a smaller impact.
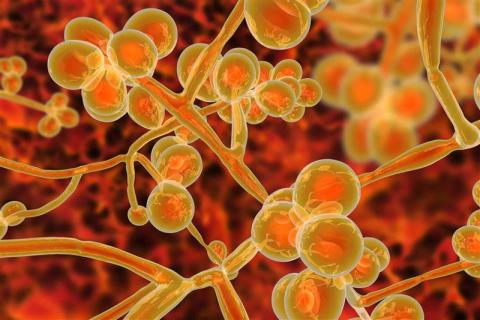
Infections caused by the fungus Candidozyma auris—formerly known as Candida auris—continue to rise, warns a report by the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). Spain reported 1,807 of the 4,012 cases in 36 European countries between 2013 and 2023, the highest number ahead of Greece (852 cases) and Italy (712), according to the survey. This microorganism spreads particularly in hospitals, causing infections that are often resistant to existing drugs.

Cosmological models suggest that matter and antimatter were created in equal amounts in the Big Bang, but in the current universe matter seems to predominate over antimatter. This imbalance is believed to be due to differences in the behaviour of the two, a violation of symmetry known as CP violation. This effect was predicted by the Standard Model of Physics and observed experimentally in mesons more than 60 years ago. Now, the LHCb collaboration at CERN, which includes significant Spanish participation, has observed this phenomenon for the first time in the decay of baryons, particles that make up most of the matter in the observable universe. The study is published in Nature.

Research analyzing data from more than 200 countries concludes that people over the age of 65 will face an increase in skin cancer cases over the next two decades. The study, published in JAMA Dermatology, used data from 1990 to 2021 and made estimates through 2050. Men and people living in countries with higher sociodemographic indices showed a higher incidence.

The KATRIN (Karlsruhe Tritium Neutrino Experiment) team has published the most accurate measurement to date of the upper limit of the neutrino mass in the journal Science, establishing it at 0.45 electronvolts (eV), less than a millionth of the mass of an electron. The KATRIN experiment, launched in 2018 in Germany, will finalise its neutrino mass measurement campaign this year, having reached 1,000 days of data acquisition.