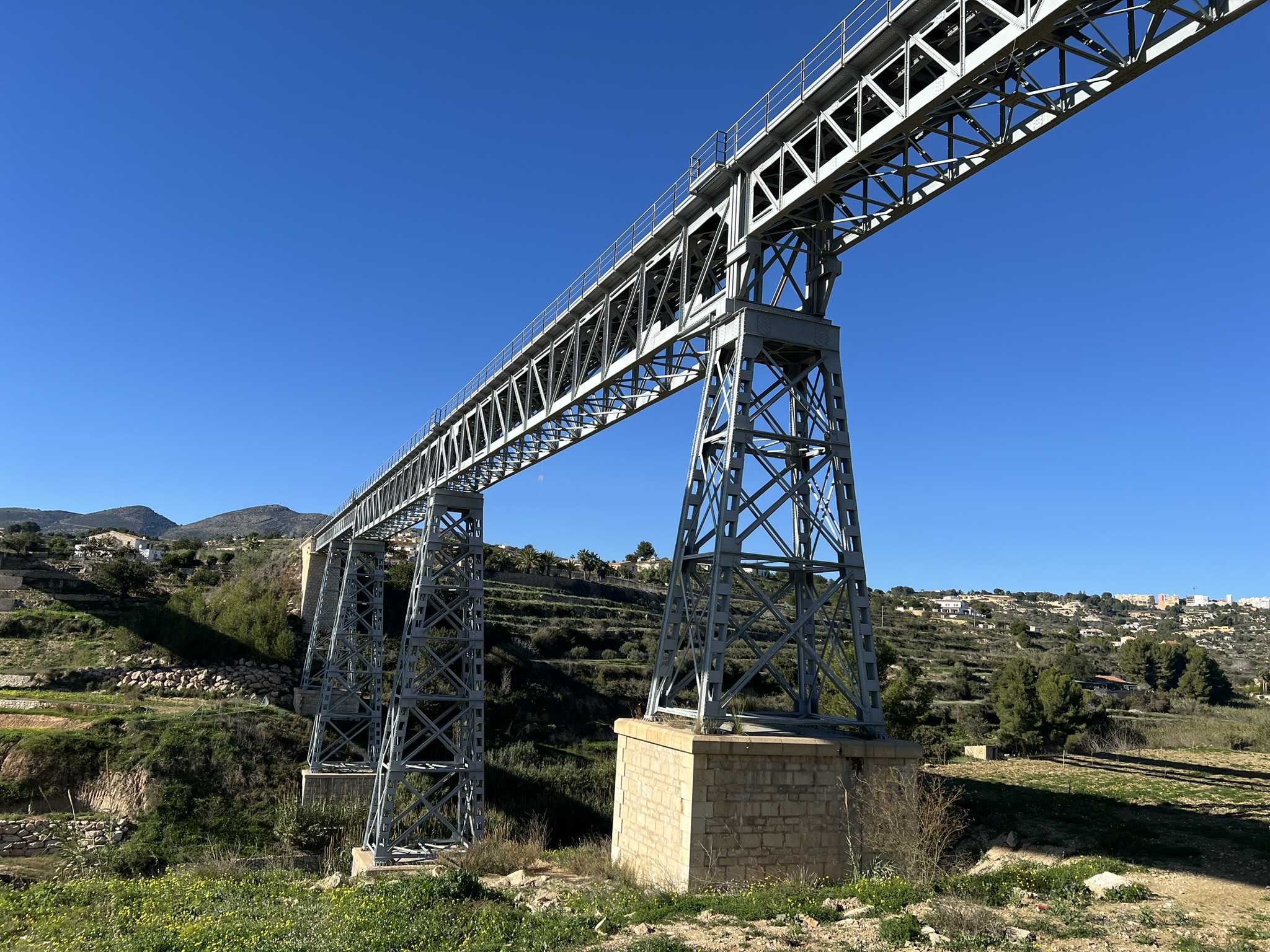
How to prevent a steel bridge from collapsing after an accident is analyzed
The twisting and bending of a steel girder bridge after a serious accident can, under certain conditions, prevent the structure from collapsing. This has been demonstrated by a team from the Polytechnic University of Valencia and the University of Vigo. Using a scale model of a steel girder railway bridge and simulations, the engineers explored the structures' response to typical damage scenarios, in which a key component is cut to simulate its failure. "These findings can be used to improve current bridge design," the authors note in the study, which is published in Nature.