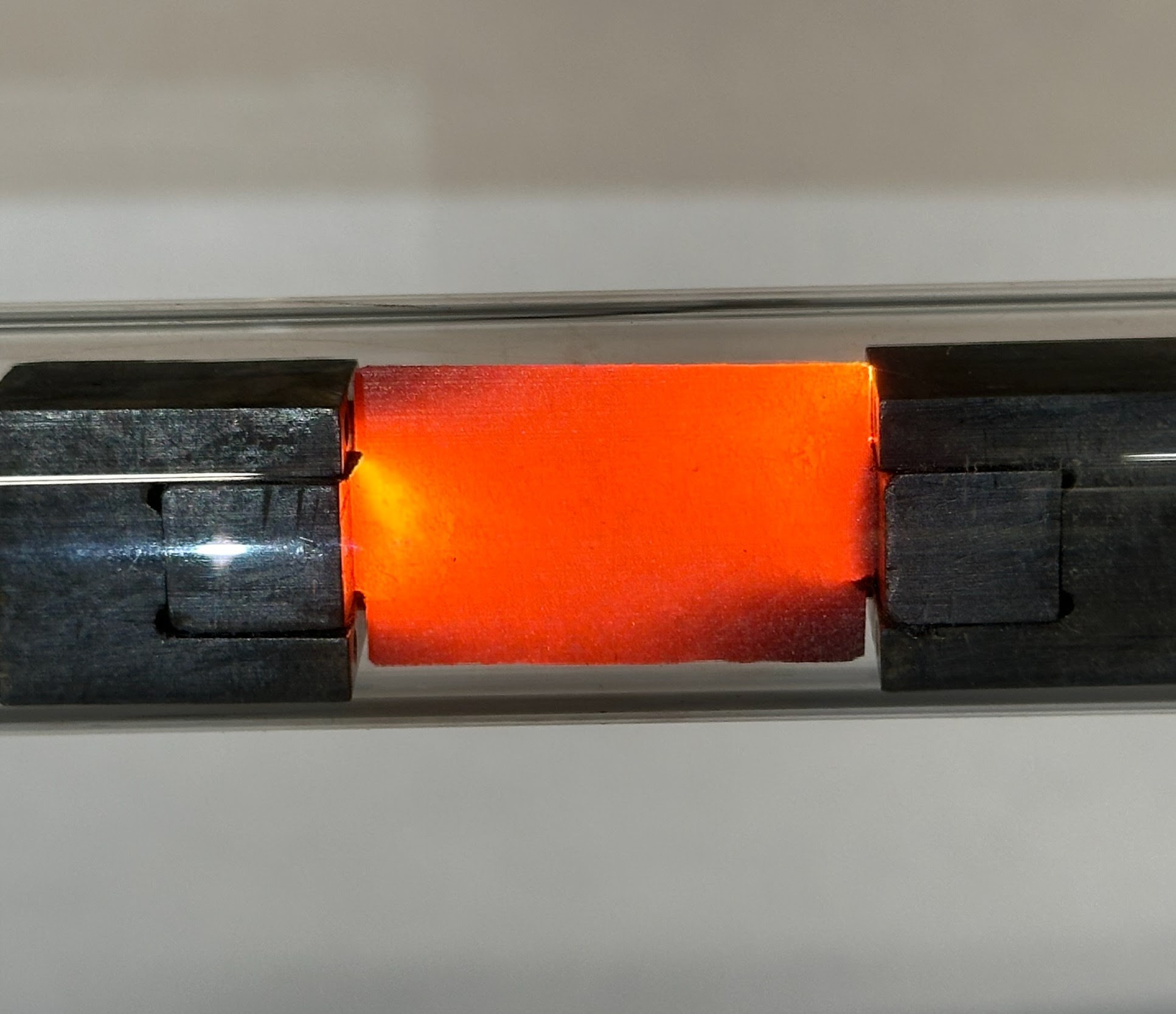
A sustainable method for extracting rare earth elements from electronic waste
A US research team has designed an ‘environmentally friendly and economically viable’ method for recovering rare earth elements from electronic waste. It is cheaper than traditional methods, uses less water, acid and energy, and emits fewer greenhouse gases, according to the authors in PNAS. Rare earth elements (REE) are a group of chemical elements needed to manufacture batteries, magnets and electronic components. Both the European Union and Spain are committed to these critical materials in order to reduce their dependence on foreign sources.