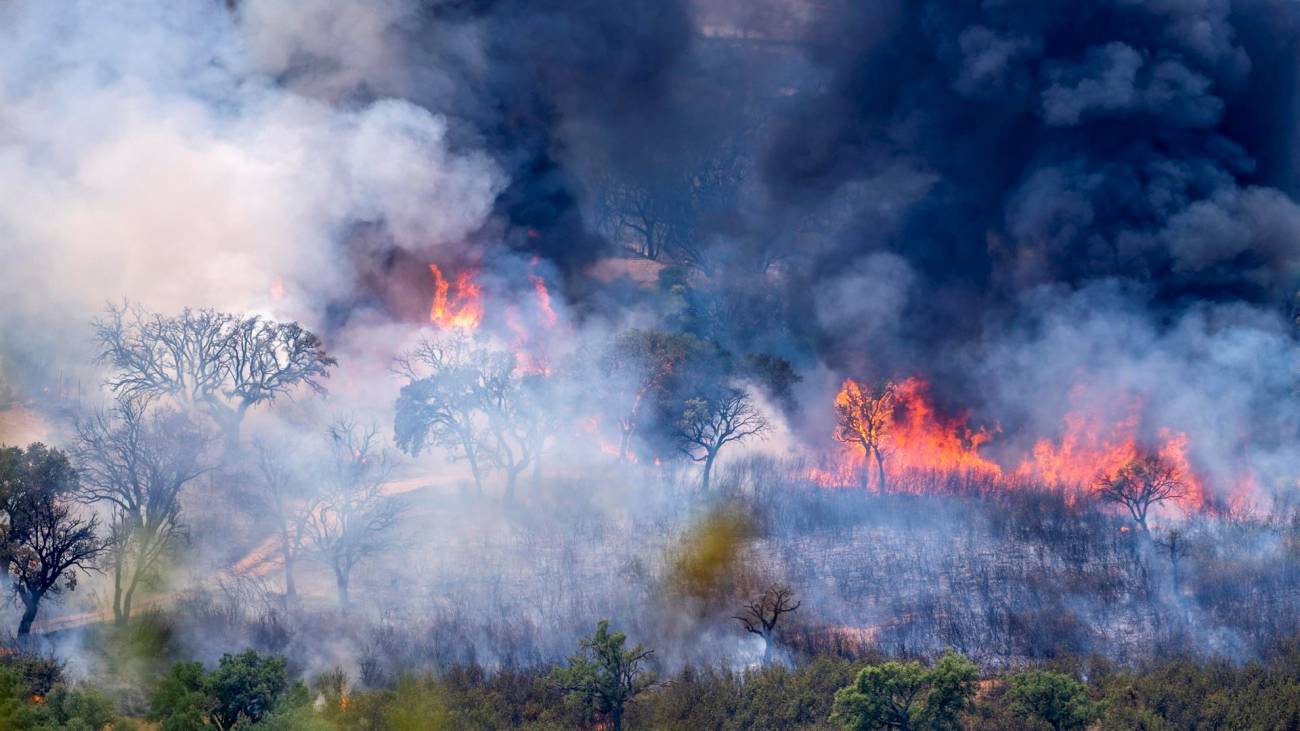
Wildfire disasters have intensified since 2015
The frequency of fire-related disasters increased significantly from 2015 onwards, according to a study analysing data from reinsurance companies between 1980 and 2023. Forty-three per cent of the 200 most damaging events, in terms of both human and economic damage, occurred in the last decade, the authors estimate in the journal Science. The risks were highest in the Mediterranean and in temperate coniferous biomes, and their frequency coincides with increasingly extreme weather conditions, they add.