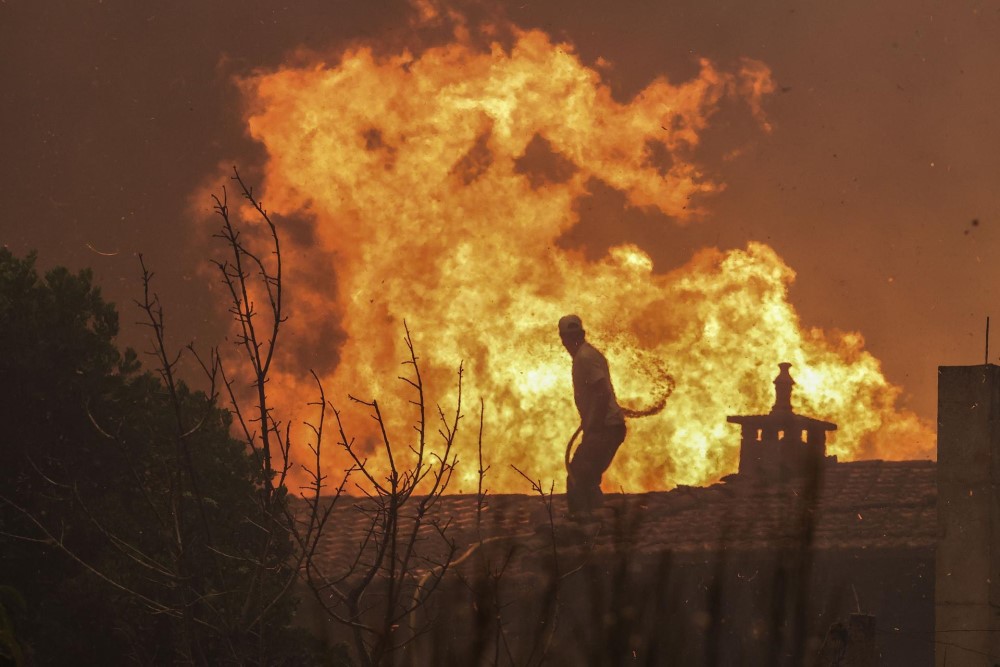
A study estimates that companies with the highest carbon emissions contributed 50% to more intense heatwaves
Using data from the 180 companies with the highest carbon emissions—fossil fuel and cement producers—research has calculated that these companies contributed 50% to the increase in heatwave intensity since 1850-1900. The authors estimate that the individual emissions of each large polluting company may have contributed to the occurrence of between 16 and 53 heatwaves. The study, published in Nature, also shows that a quarter of the heatwaves recorded between 2000 and 2023 would have been virtually impossible without anthropogenic climate change.